TB Free Workplace
TB Free Workplace NidhiSWhat is TB Free Workplace?
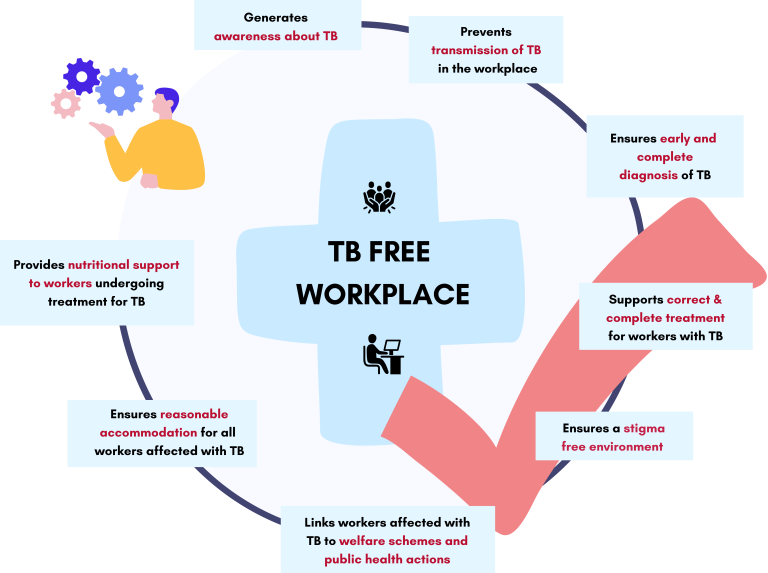
What is TB Free Workplace?A TB Free Workplace is defined as a workplace where systems are implemented to protect the workforce from TB and sufferings due to TB and it includes provisions for –
-Ensuring a stigma and discrimination-free environment for all workers affected with TB
-Generating awareness about TB among all workers
-Early & complete diagnosis of TB among the workers
-Supporting correct & complete treatment for all workers affected with TB, while respecting confidentiality of their medical information.
-Connecting workers affected with TB to social protection/welfare schemes and other public health -measures for a comprehensive care
-Providing nutritional support to all workers undergoing treatment for TB
-Preventing transmission of TB in the workplace
-Ensuring reasonable accommodation for all workers affected with TB to enable them participate or advance in employment.

How do we establish a TB Free Workplace ?
How do we establish a TB Free Workplace ?To establish a TB Free Workplace, it is essential for the senior management of any organization to first be sensitized on TB and its burden. Subsequently, make a commitment to create an environment with certain provisions where all their workers, including contractual workers: (a) have easy access to information and services on TB and workers feel confident to utilize these services; (b) have an environment conducive for prevention of TB; (c) encourage periodic screening for active TB with utmost regard for maintaining worker confidentiality; (d) workers having active TB are identified early and are put on complete treatment; (e) linked to appropriate social protection/welfare schemes and other government schemes; (f) are provided nutritional support during treatment; (g) receive leave benefits and employment protection; and (h) are not discriminated either based on real or perceived TB status. The organization can take the support of government health system and/or suitable NGOs to implement TB related activities in the workplace.

Key activities in a TB Free Workplace
Key activities in a TB Free Workplace
Employers need to demonstrate their commitment to adopt and implement a TB Free Workplace intervention. Any workplace committed to becoming a TB free workplace will have a policy/guidelines ensuring their commitment to non-discrimination on grounds of real or perceived TB status; awareness generation; prevention of TB transmission; early diagnosis; treatment initiation; support for completion of treatment; and continuation of employment relationship irrespective of the disease status. Model organization’s workplace policy is attached as Annexure7.1.

While the overall accountability of adopting and implementing the workplace policy rests with the management (Director Board/Chief Executive Officer/Managing Director), for day-to-day co-ordination and implementation of activities, it is desirable to have a workplace committee in place. TB free workplace committee needs to be established with clear terms of reference (Model ToR Annexure 7.2).
The committee needs to: -
- Prepare annual action plan related to workplace intervention for ending TB.
- Mobilize resources, including identification of volunteers, for implementation of action plan.
- Implement the interventions as per the action plan

For smaller workplaces (Up to 100 workers), if it’s difficult to establish a committee, a nodal person from the organization may be nominated to oversee planning and implementation of workplace intervention on TB. (Customise the ToR for the nodal person based on Annexure 7.2)

Peer educators are the selected workers among the workforce who, after getting trained, play a key role in the implementation of the TB programme in their workplace. They are expected to provide awareness, screening and treatment support to the workers in need. Ideally one peer educator should be there for 50 workers.
A Peer Educator should:
- be literate with formal education up to Eighth class (preferable)
- have effective communication skills & leadership qualities
- be accepted by their peers in the workplace

All peer educators need to undergo four hours of ‘Course for health volunteer and treatment supporters in NTEP’, endorsed by Central TB Division, and obtain their certificates. Peer educators engaged in other health and wellness activities at workplaces like in occupational safety and health, HIV programmes etc. can also be trained and engaged. In a workplace with a health facility, the health staff can be further equipped to become trainers for training the peer educators.

The entire workforce needs to be sensitized on the organization’s commitment to make the workplace TB Free and policy/guidelines related to it.
Awareness Messages need to focus on:
a) Organisation’s commitment to End TB in the workplace
b) Cough etiquettes and respiratory hygiene to be followed to prevent TB and other respiratory infections.
c) Symptoms and diagnosis of TB
d) Facilities for diagnosis and treatment of TB
e) Government Schemes available for workers affected with TB

Information Education Communication (IEC) activities for awareness generation could be done through posters on TB at strategic locations, health talks on TB, periodic health & wellness sessions, broadcasting messages on TB through internal Audio-Visual systems and propagating messages through social media groups.

Proper Branding of workplace interventions for ending TB will have significant impact in mobilisation of workers towards adopting healthy behaviours. This can include adopting an overarching theme such as ‘Ending TB: We are working towards it!
The TB Free Workplace theme may be adapted by workplaces themselves through consultations and then displayed in strategic locations of the workplace to inspire action and implementation of the workplan.

The management needs to establish linkages with health facilities/NGOs or equip their own health/ OSH facilities to provide the entire spectrum of TB services including testing and treatment. This could also be done in partnership with the local NTEP networks.

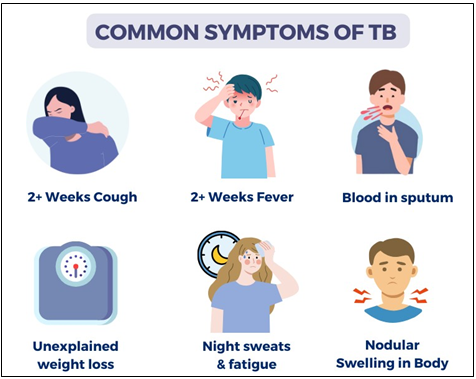
Regular screening can be conducted either by asking the workers for symptoms suggestive of TB or by taking a Chest X-ray. Anyone having any of the major TB symptoms (persistent cough for 2 weeks or more, evening rise of temperature/fever for 2 weeks or more, unexplained weight loss, complete loss of appetite, blood in sputum, night sweat & fatigue) or visible abnormalities in the Chest X-ray will be identified as workers with presumed TB. In case of occupations like mining, textile, construction, glass etc. TB screening may be done once in every quarter.
Organizations can also promote self-screening among the workers through TB Arogya Sathi Application.(https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.tb.aarogya.sathi&pcam… d=web_share)

Post screening, ensure all workers with presumptive TB are evaluated for TB. A systematic specimen collection and transportation process may be established so that specimen collected from all workers with presumed TB reaches the nearest TB detection centre for further investigations and evaluation.

It has to be ensured that all workers diagnosed with TB are promptly put on treatment at the organization health facility of the workplace or linked to the nearest NTEP health facility.
Details are available in the link: https://reports.nikshay.in/Reports/PhiDirectory

Treatment support consists of counselling, adherence support, nutrition support, psychological support, welfare schemes for workers, and linking with other social protection schemes etc. Additional customised support for the workers such as support for transportation, support for air borne infection control kits etc. may also be provided by the management. This can also be done with the support of National TB Elimination Programme.
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, through Central TB Division, has introduced the ‘Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan’ (PMTBMBA) campaign where the community is encouraged to adopt people affected with TB and support them in the form of nutritional support, nutritional supplements, additional investigations, and vocational support for a minimum period of six months or maximum period of up to three years. Workplaces are encouraged to identify Nikshay Mitras to support their workers affected with TB.
The details of PMTBMBA & the support provisioned under this are available in the link below: https://communitysupport.nikshay.in/

Management may take possible steps to provide reasonable accommodation to workers affected with TB from the loss of job/wages. This may include leave or temporary change in allotted duties to continue treatment or others as situation demands. Based on advice of the medical doctor, the worker may be encouraged to resume work once they become non-infective of TB.

Since TB is an air-borne disease, workplaces need to follow measures to control the transmission of TB among the workers. Risk assessment of workplaces may be conducted every year by a medical/nursing professional using the checklist for Air-borne Infection Control in workplaces in Annexure 7.6. Compliance to the recommendations in the assessment report needs to be ensured by the committee.

Monitoring of the activities against the annual plan need to be done routinely by the management. It has to be ensured that the information of workers diagnosed with TB is updated on a real time basis in Ni-kshay, the management information system of NTEP. It is also a good practice to publish a one-page annual report regarding the TB status and efforts to end TB in the workplace.
Monitoring indicators for workplace TB intervention: