Details of training conducted for Women Health Volunteers
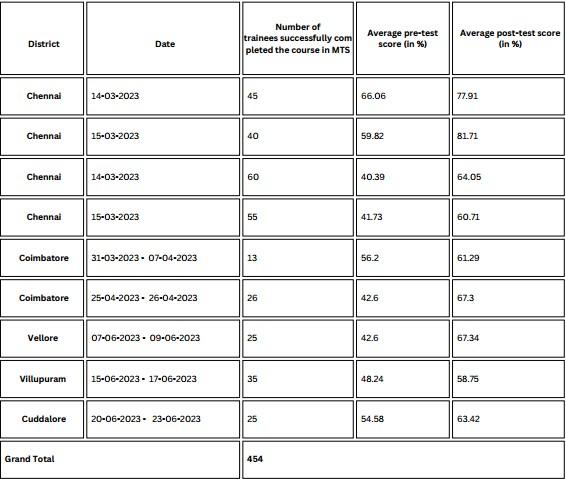
Details of training conducted for Women Health VolunteersTable 1 shows the number of Women Health Volunteers who successfully completed the course with the translated curriculum and the measures of change in pre-test and post test scores before administration of learning modules.

Conclusion
Conclusion
|
Image

|
STDC Tamil Nadu has demonstrated a system for translating the contents into regional language, which is replicable. Involvement of State Training Division, State Public Health Department and National Health Mission has ensured ownership from all the stakeholders. The meticulous execution of training using translated materials with adequate linguistic and cultural inclusivity, ensured that the health volunteers were able to obtain new learning and skills which are instrumental to their roles in TB prevention and care. Conducting the course in Tamil ensures that vital information is effectively communicated to the target audience. Experience from phase-1 has shown that it is feasible to train the health volunteer through modernize training system, This may help to reach out more number of health volunteers within short span of time. The "Tamil Nadu-Experience of Using the Modernized Training System for Training Health Volunteers" is a transformative initiative poised to make a lasting impact on TB prevention and care in the state. By combining cutting-edge technology with cultural sensitivity, this experience sets a benchmark for training of Health volunteers. |