Style Guide
Style GuideThe style guide provide reference to what standard styles should be used while developing content. This would ensure uniformity of content appearance and will ensure that the trainee would identify the content as belonging to a whole. The style guide would specify standard content styles that can be applied to online content. This would include the following. ( Click the item to read more.)
- Formatting Guide - (Note: Work in Progress)
- Basic Color Palette
- Text (Headings, Bullets and numbering, Quotes, Captions)
- Tables
- Images(Pictures/ photographs/Graphics)
- Library of standard graphics
- Videos and Animations
- Language Guide (TB inclusive Language)
Formatting Guide
Formatting GuideEnsuring consistency and professionalism in the content on the platform is crucial for an effective learning experience. Adhering to specific formatting guidelines helps maintain clarity and coherence in the content.
File Location: Search for specific course materials or content pages within knowledge base platform. It involves navigating through various parameters or criteria to pinpoint the desired information. In the context of our platform, locating a file entails searching for a particular content page based on factors such as page ID, title, status, creator ID, or tags.
- Page Library: The Page Library provides a means to locate files based on various parameters, including status (published on LMS, approved, final review etc.), page tags (content overload, for upgrade, grammar check etc.) , page ID, content creator ID, and title, among others. Users can input any combination of these parameters to find the desired content page. Access to the Page Library is available through the provided link- https://ntep.in/PageLibrary .
- Knowledge Map: To access files, users can search for the content page title within the Knowledge Map. They can then refine their search based on the status of nodes (pending review, live, depreciated), if needed. Utilize the provided link- https://ntep.in/km-nodes to navigate to the Knowledge Map.
- Curriculum: Access the approved courses as well as those under development by navigating through the provided link- https://ntep.in/curriculum?field_grouptype_target_id=40 . This link grants access to a variety of content pages associated with these courses, including nodes and sub-nodes.
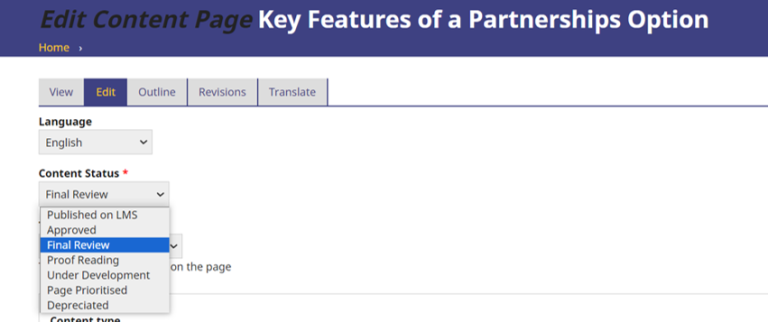
After identifying the desired content page, attention should be given to several parameters including content status, content type, page tags, content creator, and revision information. Before proceeding to translate HTML content to H5P or modify existing H5P content, it is crucial to ensure the correct content status is selected.
Further details on other parameters will be provided after explaining the content type.
Content Type (Course Presentations): H5P offers diverse content types catering to various interactive needs, facilitating easy creation of engaging materials. For detailed information, refer to https://h5p.org/content-types-and-applications. Our focus here is on course presentations, where we'll create interactive slides to enhance engagement and learning.
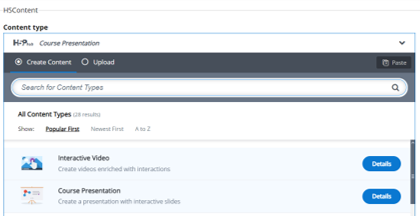
Ensure that the HTML content utilizes course presentations, with each presentation containing a maximum of 7 slides. If accordion or column formats have been used previously, maintain them without making any alterations.
Below is a thorough guide to assist you in creating or editing content pages while ensuring they meet the required standards:
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|
1. |
Font Size |
Content title: 100% (Bold) Image
Image
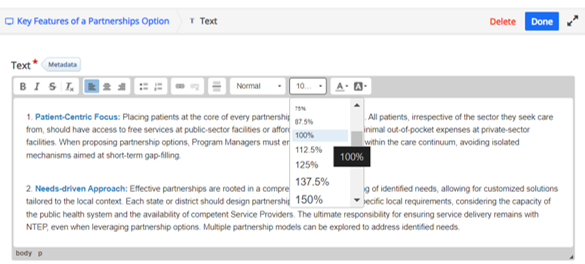
|
|
2. |
Margin |
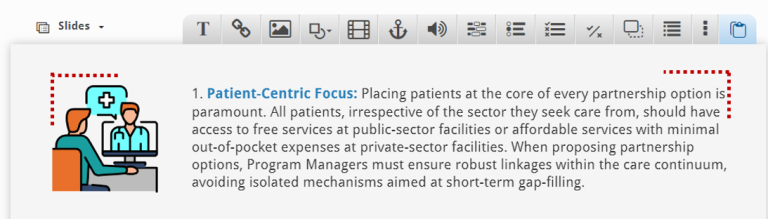
1 cm (as indicated by the red lines in the content page provided) Image
|
|
3. |
Color Scheme |
Blue (sharp blue), orange (carrot) or green (emerald green) Image

|
|
4. |
Videos |
Download the videos embedded within the HTML content and then upload them onto the course presentation for integration. Image
Image
|
|
5. |
Infographic |
Image

Image
For new infographics, if the text isn't clear on existing figures, utilize templates available at https://www.presentationgo.com/ . Upload only the image of the template (e.g., triangle, hexagon) to the H5P software. Add text separately on H5P after uploading the template image. Image
Note: |
|
6. |
Icons |
You have the option to use https://www.flaticon.com/ for icons. Additionally, you can employ separators like horizontal or vertical lines to distinguish content text from the icons. Image

|
Language Guide
Language GuideThe Language guide is primarily extracted from the 'Words Matter' document (Second Edition published by StopTB Partnership in 2022, https://conf2022.theunion.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/stbp_words-mat…). Its use has been envisioned to guide the accommodation of inclusive language for TB training & communication while developing & reviewing course content under the Modernised Training System. Categorized into 'Alternatives', 'To be Carefully Used' and 'Emerging Terms', the guide underlines terms that 'must be replaced or alternatives that are sensitive and inclusive, use of terms that must be re-considered and other emerging terms in TB.
Alternatives
|
Use |
Replace |
Comments |
| They/them | He/him, She/her | More inclusive & gender sensitive |
| Contact Person | TB Contact | Does not have strong negative connotations but is not person-centered |
| Person Lost to Follow Up | Defaulter | Unnecessarily and unfairly places blame on the person receiving treatment |
| Noncitizen resident or Unauthorized resident/worker | Illegal/Alien worker | Offensive & isolates their access to TB treatment & care |
| Person with presumed TB | TB Suspect | Negative association |
| TB Prevention & Care or Ending TB | TB Control | Its continued use is no longer recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) not people-centered, ignores contributions of communities & people affected by TB, -ve connotations of TB authorities as being in full control of all aspects of prevention, treatment & care |
| PLHIV/AIDS PLHWA/Person living with HIV | AIDS Patient | Necessary to reflect the fact that an HIV-positive person may continue to live well and productively for many years |
| Person Living with HIV/AIDS | Innocent Victim | The term wrongly implies that people infected in other ways (other than those infected medically or at birth through no fault of their own) are somehow guilty. |
| Person/s with physical disability | physically challenged | The term ‘physically challenged’ is deemed inappropriate as it places focus on the identity rather than the person & their barriers |
To be carefully used
|
Use |
Use carefully |
Comments |
| Person with presumed TB | Presumed Presumptive | The term ‘Presumed Presumptive’ places emphasis on the disease and not the person with possible tuberculosis. While, it can be used to describe a stage in the process of diagnosing TB, when discussing an individual, it is best to say a person with presumed TB |
| Burden | It should be stressed that it is the disease, not the people affected by the disease, that burdens a country, a region or the world | |
| Case Finding/Case Detection | Activity occurs by virtue of action taken by the person experiencing symptoms | |
| People deprived of their liberty | Prisoner/Inmate | An alternative can be ‘People deprived of their liberty’ (in some contexts it can stigmatize people and can impact perceptions regarding the right to health for all |
| Compliance, Non-Compliance | Noncompliance unfairly assigns blame to the person receiving treatment when many external factors outside a person’s control may be the cause | |
| Adherent/Nonadherent | Unfairly assigns singular responsibility for treatment completion to the person receiving treatment, when many external factors outside a person’s control | |
| Mobile Worker | Refers to a large category of persons who may cross borders or move within their own country on a usually frequent and short-term basis for a variety of work-related reasons, without changing their primary residence or home base | |
| Bacteriologically +ve/-ve | Sputum/Smear Positive/Negative | Smear microscopy is no longer recognized as a recommended diagnostic strategy. The preferred term is bacteriologically positive/ negative |
| Key and Vulnerable Population | Risk Groups | While the term is used in the epidemiology of TB to describe clinical risk groups when discussing an individual or group, it is best to say key and vulnerable populations . |
| Person Affected by TB/Person on Treatment/Client | Patient/TB Patient | Patient/TB Patient ‘clinicalizes’ them and focuses on the treatment process rather than the person |
Emerging Terms
|
Terms |
Definition |
| COVID-19 | An infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. COVID-19 was first reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019 |
| Bi-Directional Testing | The delivery of simultaneous diagnostic testing for more than one disease |
| COVID-19 Response Mechanism (C19RM) | A special initiative of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, TB and Malaria to provide countries with additional funding to respond to COVID-19 to mitigate its impact on HIV, TB and malaria programs and to initiate and strengthen improvements in health and community systems |
Setting learning objectives
Setting learning objectivesThis document outlines the principles for stating learning objectives for each KM Node.
Following are the steps for defining learning objectives.
- Clearly outline the anticipated outcomes that learners will be able to demonstrate after engaging with each page.
- The learning objectives should be stated such that it correspond to these outcomes. It should guide what the content page should represent. Specify what learners will be able to do, ensuring that objectives:
- clearly defined or describes an action
- are measurable
- Ensure that objectives are learner-centric, focusing on the behaviors that learners should adopt after going through the content, rather than focusing on what the page will “teach”
- Incorporate action words from the Modified Bloom’s Taxonomy (see reference table below).
- Choose an action word from the various levels of objectives (Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, Evaluation) when formulating learning objectives, aligning them with the educational activity's overarching goal.
- Refrain from using vague terms like understand, learn, and know, as they lack measurability due to the absence of tangible outcomes.
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measurable Verbs:
Benjamin Bloom devised a taxonomy of measurable verbs to facilitate the description and categorization of observable knowledge, skills, attitudes, behaviours, and abilities. This theory posits that there exist discernible levels of observable actions indicative of cognitive activity within the brain. Through the utilization of measurable verbs in crafting learning objectives, the explicit actions required to demonstrate learning are articulated.
Table 1: Measurable verbs
|
Category |
Meaning |
Verbs |
||
|
Knowledge |
Remember previously learned information. |
Arrange Choose Cite Define Describe Draw Enumerate Identify Indicate Label List
|
Locate Match Name Order Outline Quote Read Recall Recite Recognize Record
|
Relate Repeat Reproduce Review Select State Study Tabulate Tally Tell Underline Write |
|
Comprehension |
Demonstrate an understanding of the facts. |
Articulate Associate Characterize Clarify Classify Compare Compute Contrast Convert Defend Describe Differentiate Discuss Distinguish Estimate Example |
Explain Express Extend Extrapolate Factor Generalize Give Give examples Identify Illustrate Indicate Infer Interpolate Interpret Locate Match Observe |
Organize Paraphrase Predict Recognise Relate Report Represent Restate Review Rewrite Select Summarize Tell Translate
|
|
Application |
Apply knowledge to actual situations. |
Acquire Act Adapt Apply Ascertain Assign Avoid Back Back up Calculate Capture Change Chart Choose Classify Complete Compute Construct Consult Convey Customise |
Demonstrate Develop Discover Dramatize Derive Employ Experiment Explain Execute Generalize Guide Identify Illustrate Implement Interpret Interview Manipulate Modify Obtain Operate Organize |
Paint Perform Practice Predict Prepare Produce Process Provide Relate Schedule Select Show Simulate Sketch Solve Translate Use Utilize Write |
|
Analysis |
Break down objects or ideas into simpler parts and find evidence to support generalizations. |
Administer Analyze Appraise Break Break down Calculate Categorize Chart Classify Compare Conclude Confirm Contrast Correlate Corroborate criticize Identify Illustrate Infer Inspect Debate |
Deduce Delegate Detect Diagnose Diagram Differentiate Discover Discriminate Dissect Distinguish Divide Document Ensure Establish evaluate Examine Experiment Figure Group Inventory Investigate |
Manage Monitor Order organize Outline Point out Predict Prioritize Question Reconcile Relate Resolve Select Separate Solve Subdivide Survey Test Transform Troubleshoot |
|
Synthesis |
Compile component ideas into a new whole or propose alternative solutions. |
Anticipate Appraise Argue Arrange Assemble Assess Brief Attach Choose Collect Compare Compile Conclude Consolidate Construct Contrast Core Counsel Create Criticize Critique Decide
|
Defend Describe Depict Design Develop Determine Discriminate Enhance Estimate Evaluate Explain Facilitate Formulate Frame Generate Grade Handle Invent Judge Manage Mediate Modify
|
Organise Prepare Prescribe Probe Propose Rate Rearrange Reconcile Refer Relate Release Reorganise Revise Rewrite Select Set up Specify Supervise Synthesize Test Value Verify Weigh |
|
Evaluation |
Make and defend judgments based on internal evidence or external criteria. |
Appraise Argue Arrange Assemble Assess Categorize Choose Collect Combine Compare Compile Compose Conclude Construct Create Design Develop Devise Estimate Evaluate
|
Explain Facilitate Formulate Generalize Generate Hypothesize Improve Integrate Invent Judge Justify Make Manage Measure Modify Organize Originate Plan Predict Prepare
|
Produce Propose Rate Rearrange Reconstruct Relate Reorganize Revise Rewrite Role-play Score Select Set up Specify Summarize Support Synthesize Tell Tell why Value Write |