STDC Delhi- Operational Research under NTEP: Learnings from New Delhi Tuberculosis Centre
STDC Delhi- Operational Research under NTEP: Learnings from New Delhi Tuberculosis CentreINTRODUCTION
India accounted for more than 25% of the global TB burden. To End TB, various interventions are planned by the Centre and State under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP).1 Operational Research is one of the requisites to generate continuous evidence to ensure state strategies are aligned well with the National Program. This evidence informs change in interventions or policy and optimize implementation of program activities to improve overall health outcomes.2
The National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination in India encourages and promotes Operational Research (OR) activity. Central Tuberculosis Division (CTD) has published areas and priorities for operational research at state, zonal and national level. The ‘Revised Norms and Guidelines for STDC’3 recommend STDCs to independently plan and execute need-based operational/implementation research and inform effectiveness of interventions at State.
However, most of the STDCs in the country are unable to conduct research activities due to underlying deficiencies in the systems or capacities. STDC Delhi has been conducting research studies regularly. Most of the projects have been conducted in collaboration with Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), National Institutes for TB, Medical colleges at New Delhi, Delhi TB-Association and development agencies like FIND (the global alliance for diagnostics), The UNION (International Union Against TB and Lung Disease), MRC-London (Medical Research Council), Centre for Equity etc. Around one-third of the total research projects undertaken by STDC Delhi in past 7 years are Operational research projects.
Since 2016-17, 102 research projects have been published as formal research papers, 56 of them have been published in the past 3 financial years. Some of the findings from these research studies have been incorporated into practice under NTEP. Findings from studies like National Sample survey for TB in 1950, eight longitudinal disease prevalence surveys conducted in domiciliary area of STDC Delhi for over 30 years, Active Case Finding (ACF) campaign in homeless pavement dwellers along Yamuna Pushta with mobile X-ray van supported by Medanta Medicity in Gurugram4 and prevalence of initial and acquired drug resistance and outcomes of Short-course chemotherapy (SCC) are some of them.
STDC Director and the staff has participated in 889 scientific events in last decade (since 2014-15) which has resulted in collaborations, cross-learning, funding and more research opportunities. The staff has gone an extra mile in presenting their research projects and findings at National (19) and International (13) scientific platforms. This document captures the experiences of STDC Delhi in conducting an operational research and key learnings. The enabling factors are listed in detail as an information for other STDCs to enhance replication and uptake.
STDC Delhi
Established in 1940 by Government of India and TB Association of India4 (TAI) jointly, officially known as New Delhi TB Centre (NDTBC) functioned as a model clinic for initiating organized domiciliary treatment for TB. In 1951, the center upgraded to first TB Training and demonstration center (TDTC) to provide training to health care workers and diagnostic referral center for five northern states until formal declaration as an STDC in 2005. Since then, STDC Delhi has been actively promoting operational research with the prime objective of evolving patient friendly and cost-effective treatment to people with TB. The details of the research activities and projects may be assessed from the annual reports published by STDC Delhi.4
1.https://tbcindia.mohfw.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/5646719104TB_A…
2.theunion.org/sites/default/files/2024-06/Union OR to Improve Health Services 2nd 2024.pdf
3.https://tbcindia.mohfw.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Norms-and-Guid…
4.https://www.ndtbc.com/annual-report
Enabling Factors For Conducting Operational Research at STDC Delhi
Enabling Factors For Conducting Operational Research at STDC Delhi1.Human Resource: STDC Delhi developed its full-fledged sections in epidemiological, public health, statistical and administrative wing. The STDC director provides leadership and guidance to opportunities for conducting research. The Epidemiologist at STDC serves as the nodal officer for implementation of research. He is supported by a microbiologist and a biostatistician for monitoring collection and analysis of research data.
2.Capacity Building on OR: The key staff along with STDC Director completed their formal training in research methodology in 1990 and ‘How to do Operational Research?’ in 2005 at National Tuberculosis Institute, Bangalore.
3.Financial Resources: Along with funds earmarked for operational research in State NTEP funds, STDC Delhi shares experience of trying odds with every opportunity to fund its research. In last 10 years, more than 50% of the total researches were funded by State Operational Research Committee. In addition, some research projects are funded by ICMR or external agencies like MRC London, Corporates like Sandoz under corporate social responsibility (CSR). Funds earmarked for research studies are restricted to use under the same functional component.
4.Infrastructural capacity: Accredited with National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL), the Intermediate reference laboratory (IRL) at STDC Delhi is equipped with Biosafety Level-3, Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS), second-line Line Probe Assay (LPA) and Liquid culture DST (drug-susceptibility testing) facilities. These make STDC Delhi a preferred site for research projects meant for multi-centric clinical trials, kit validation or validation of new diagnostic modalities4 in collaboration with RBIPMT (The Rajan Babu Institute of Pulmonary Medicine and TB), NITRD (the National Institute of TB and Respiratory diseases) or NIRT (National Institute for research in Tuberculosis, Chennai).
5.Orientation to potential researchers: STDC Delhi regularly conducts orientation workshops for potential researchers (DTO), faculty from various medical and nursing colleges, development agencies and corporate entities to sensitize on potential areas for operational research. Guidance on research tools to support good quality data collection is circulated.
6.Institutional mechanisms: STDC Delhi has established an institution level 7-member Scientific Advisory Committee, that reviews and finalizes the research proposals to be submitted to Operational research committee on behalf of STDC Delhi.
STDC Delhi has its own Institution Level Ethics Committee4 with members represented from TB Association of India, Delhi TB Association, State level Legal advisor, Community member, STDC itself and chaired by a Medical College faculty. The committee reviews the submitted protocols and provides ethical clearance based on the type of research involved.
7.Collaboration with State OR mechanism: STDC Delhi remains the focal point for organizing state task force meetings. The State Operational Research committee meets at STDC Delhi regularly to review and finalize the submitted proposals. Hence, any upcoming/ ongoing research is informed to STDC Delhi and priorities for conducting the same is facilitated. The State Task force also advocates for one thesis per medical college in a year to be undertaken by postgraduates.
8.Collaboration with TB Association of India (TAI): The staff of STDC Delhi provides managerial support to TB Association of India. They support the publication of the quarterly journal of TAI as members of editorial board4. Also, the faculty actively participates in annual conferences organized by TAI and supports in finalizing the scientific program and participating in the sessions. This provides an opportunity for STDC Delhi to create more awareness in their staff regarding current priorities of the national program, learnings from other states and dissemination of their research findings.
9.Maintaining a database of research studies: STDC Delhi documents the database (offline & online) of TB related (past and ongoing) research activity conducted in state. It is maintained as a part of the program annual report documented by STDC. It helps in wide dissemination of undergoing projects and provides an opportunity for collaboration, cross-learning or enhancement of research. Details of the research projects taken up in 2022-23 are listed in the annexure.
10.Dissemination of findings: STDC Delhi encourages use of various media to disseminate their research findings to the community at large. Around two-thirds of the total publication (71) is disseminated each through research publication or review article in past 6 years. This helps to keep the team motivated and continue to uptake further research projects.
Key Learnings
Key LearningsInvolvement of District Tuberculosis Officers: STDC Delhi encourages participation of District Tuberculosis officers (DTO) in conceptualization of research topics, implementation of research, training the project staff and monitoring the data collection. Inclusion of DTOs in the research team lays off any administrative issues related to data collection and absorption of research findings into practice.
Technical expertise from Medical College: STDC Delhi actively participates in approaching Medical College faculty for their technical expertise. Many research projects are planned in the form of thesis/ research work/dissertation as a part of the students’ medical programme curriculum. Having principal investigators or co-lead from the medical college adds value to the research topic and benefits the programme.
Supervision and Monitoring: Frequent supportive supervisory visits are conducted by STDC staff in the project area. The challenges in implementation are discussed and strategies are realigned, if necessary. The State OR committee regularly conducts mid-term review of the ongoing research studies.
Sustainable and resilient systems: STDC Delhi have worked around creating and sustaining institutional mechanisms that are not individual dependent. The processes for conducting an operational research at STDC Delhi has evolved and defined with time. It is elaborated in diagram below. Any operational research in the State is well informed to STDC and every activity is well coordinated with support from State TB Cell. The steps include collaboration with multiple stakeholders and their technical experts. Mechanisms to receive funds for research projects are well identified for smooth disbursement.
Process flow diagram for conducting Operational Research at STDC DELHI
Process flow diagram for conducting Operational Research at STDC DELHI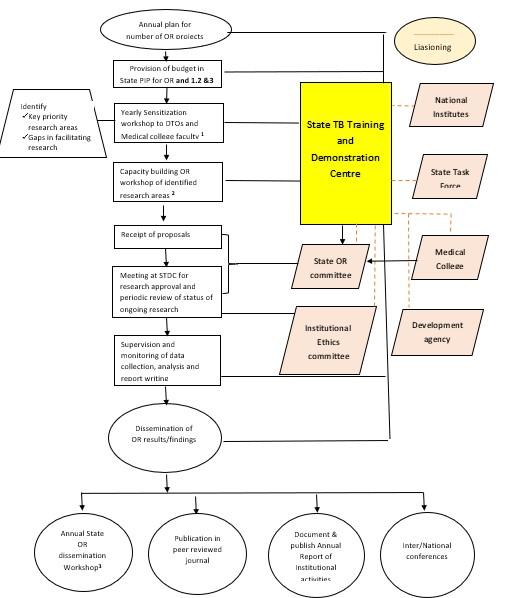
Few challenges on timely release of funds due to delay in in receipt of utilization certificate from other institutions have been reported. The STDCs need to anticipate such challenges and be prepared accordingly for smooth completion of research.
List of research activities supported by STDC Delhi in 2022-23
List of research activities supported by STDC Delhi in 2022-23|
S.no |
Title |
Study area |
Type of research |
Source of funding |
|
1 |
Mapping of Anti-Mycobacterial Drug Resistant Hotspots under NTEP in Delhi State |
STDC Delhi & TAI |
Operational Research |
Delhi State OR Committee |
|
2 |
TB prevalence & interventions for reducing TB and LTBI in high-risk key population of rickshaw driver & construction workers |
Selected districts of Delhi |
Operational Research |
ICMR |
|
3 |
Prevalence, risk factors and laboratory diagnosis of non-tuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) disease: A multicentric study |
IRL, STDC Delhi and 5 other sites in country |
Multi-centric trial |
ICMR |
|
4 |
Short intensified treatment for children with tuberculous meningitis (SURE) |
IRL, STDC Delhi and Kalawati Saran Children hospital, New Delhi |
Clinical Trial |
MRC, London, UK and National Institute of Health Research |
|
5 |
Evaluate the effectiveness, safety and tolerability of various Linezolid in combination with Bedaquiline and Pretomanid in Adults with Pre-Extensively Drug-Resistant or Treatment Intolerant/Non-responsive Multidrug-Resistant (MDRTI/NR ) Pulmonary TB in India. |
IRL, STDC Delhi and RBIPMT, New Delhi |
Clinical Trial |
ICMR |
|
6 |
Assessment of effectiveness of the 4-month Moxifloxacin containing daily regimen in the treatment of microbiologically confirmed new pulmonary TB patients |
IRL, STDC Delhi and TB Chest clinic at Lok Nayak Hospital |
Clinical Trial |
ICMR |