Content Status
Type
Linked Node
Catalase peroxidase test for MTB
Learning ObjectivesDescribe principle, result and interpretation
Catalase Peroxidase test for MTB
Principle:
Catalase is an intracellular, soluble enzyme that splits hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The oxygen bubbles into the reaction mixture to indicate catalase activity. Virtually all mycobacteria possess catalase enzymes, except for certain isoniazid–resistant mutants of M. tuberculosis and M.bovis.
Mycobacteria possess several kinds of catalase that vary in heat stability. Quantitative differences in catalase activity can be demonstrated by the 680C test at pH 7 (indicates loss of catalase activity due to heat). Drug susceptible strains of M. tuberculosis lose catalase activity when heated to 680C for 20 minutes. For these tests, cultures on LJ should be used.
Controls:
Check reagents by testing extract from an uninoculated tube of medium (negative control).
- 1. 0.067M phosphate buffer solution, pH 7.0
Solution 1:
Na2HPO4, anhydrous :9.47 g
Distilled water: 1 litre
Dissolve disodium phosphate in water to make a 0.067 M solution.
Solution 2:
KH2PO4: 9.07 g
Distilled water :1 litre
Dissolve in water to make 0.067 M KH2PO4 solution.
Mix 61.1 ml of Solution 1 with 38.9 ml of Solution 2. Adjust the pH to 7.
2. Hydrogen peroxide, 30% solution
Store in the refrigerator.
Tween- 80:10 ml
Distilled water: 90 ml
Mix Tween-80 with distilled water and autoclave at 121o C for 10 minutes.
Allow to cool. Store in the refrigerator.
4. Complete catalase reagent (Tween-peroxide mixture):
Immediately before use, mix equal parts of 10% Tween-80 and 30% hydrogen peroxide.
Use 0.5 ml reagent for each strain to be tested.
Procedure:
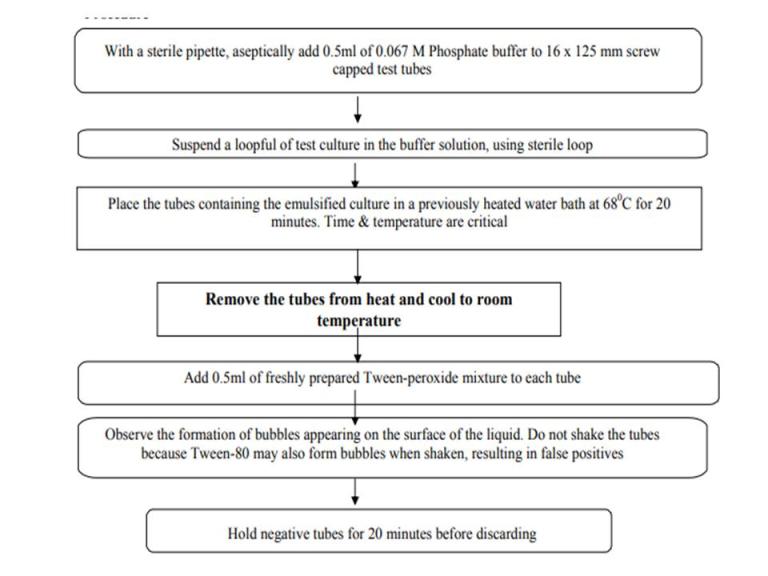
Results and interpretation:
If bubbles appear (due to the production of oxygen gas), the bacteria are catalase positive.
If no bubbles appear, the bacteria are catalase negative.
Resource
Assessment
|
Question 1 |
Answer 1 |
Answer 2 |
Answer 3 |
Answer 4 |
Correct Answer |
Correct Explanation |
Page id |
Part of Pre-Test |
Part of Post-Test |
|
All mycobacteria have catalase enzymes. |
True |
False |
|
|
False |
All mycobacteria possess catalase enzymes, except for certain isoniazid–resistant mutants of M. tuberculosis and M.bovis. |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
Question 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
During the formation of bubbles, do not shake the tubes. |
True |
False |
|
|
True |
The tubes should not be shaken because Tween 80 may also form bubbles giving false positive results.
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Content Creator
Reviewer
Target Audience
- Log in to post comments