NTEP Training System
NTEP Training SystemThis online live document is about the NTEP's training system.
The Training System brings systems thinking into training in a modern way. It incorporates modern methods of training material creation, training delivery and monitoring and evaluation of training while including the best practices of traditional techniques. It is inclusive to all stakeholders working in the fight against TB in India such that training material created through discrete efforts can be pooled into a larger whole. The system also accounts for the continuous evolution and expansion of the program and is agile to accommodate the evolving training needs.
The system comprises three interoperable components, each dealing with 1) content creation 2)Training Operations 3)Training Monitoring and Evaluation and competency assessment. This model of separation of purposes ensures that Training content development and maintenance, can continue, without creating a dependency on training operations, while delivering the latest material. Simultaneously it offers a standardized way to plan, monitor, evaluate and conduct training needs assessments as a part of the dynamic and ever-changing training material and operations.
The components use open-source standards that enable complete interoperability at a low cost. For example, the training material output from the content creation component is embedded in various externally maintained Learning Management Systems such as, the WHO's Swasth-eGurukul or the NIHFW's Saksham. The system also lays the foundation for future Ai-based-on-demand training, where any user should be able to intuitively query in natural language, and receive the most relevant and contextually adapted programmatic instruction/ training.
The Need to modernize training in NTEP
The Need to modernize training in NTEPNational Tuberculosis (TB) Elimination Program (NTEP) of India is one of the largest public health programs in the world. It has over 30,000 peripheral health institutions providing diagnostic and treatment services in the public sector, with a huge workforce of Medical Officers, Paramedical staff, Multi Purpose Health Workers, and other frontline health workers. Putting this together with incentivised volunteers and a huge private sector, the quantity and variety of human resources is at a scale that is unparalleled. Trained Human Resource (HR) is critical for ensuring TB patients receive quality diagnostic, treatment and other patient support services.
The program has considerably expanded in the last five years into many new technical areas such as Direct Benefit Transfers and TB Preventive Therapy. There has been a corresponding increase in the amount training is needed. These areas are continuously evolving, with very frequent updates and changes. As a result of this there is a regular need for training, to rapidly disseminate changes and additions in program operations. The current training system primarily consists of 9 printed modules which are delivered in a modular reading fashion; updates over and above these modules are disseminated using guidelines/ other documents. In addition a variety of training material is also created by a multitude of development partners operating in different geographies in specific thematic areas. This material is used for training in the form of formal training, orientation workshops and sensitization meetings. The training status of core NTEP staff is monitored using aggregate reports collected manually from the TU level.
There is a felt need to better organize, increase the pace and efficiency at which program evolution is communicated to the field in the form of training. This revision of the training system should:
- Upgrade the current paper based training material to use a combination of electronic multimedia, organizing efforts of many stakeholders into one uniform system of content development.
- Use modern methods of knowledge and skills transfer including e-learning and adult learning principles. This would also need to leverage the increased acceptance to electronic modes of training, a change brought about by the COVID19 pandemic.
- Have a low effort monitoring system that can be applied across the country.
With these needs in mind NTEP had decided to revise and modernize its training system. The subsequent sections discuss the various components of the system and the various standard processes and guidelines related to them.
Strategy for Modernizing Training
Strategy for Modernizing TrainingThe needs described in the previous section can be strategically addressed under three themes, Content Development, Training operations and M&E of training. To address these needs effectively, the Modernized Training has three sub-systems and protocols working seamlessly with each other. These are:
- Training content creation: This is first part, where there are systems and processes to create, update and maintain a repository of various training concepts and related standardized training content, along with other documents (guidelines, directives, etc). This would involve an online system called the Knowledge Base. This would be operated by a central team of experts and content creators, who maintain the knowledge base and its contents.
- Training Operations: This component is where the actual training is performed using content prepared. It will include processes such as planning and execution of training and certification. It would include an online Learning Management System (LMS) such as Swasth-eGurukul. This would be operated by trainers and trainees from across the country to deliver and receive training.
- Monitoring and evaluation of training: This component allows the monitoring of the ongoing training in real-time against the general goal of all human resources related to NTEP are "Trained". This would require the maintenance of training information of all related personnel and generate reports or dashboards to monitor the progress/ current status. This would need an online tool for managing the training information of all personnel, including training history and certifications and a dashboard where data can be visually explored to understand the status of training across the country. This system would also include process of training supervision and evaluation and identifying which personnel requires re- or update training.

Subsystem 1: Content Creation
Subsystem 1: Content CreationThe first subsystem of the modernized training system is the machinery to develop translatable multi-media training material that can be used for training all personnel across the country. The material developed needs to be:
- standardized and translatable(to ensure consistent messaging/ practices) accessible openly in an electronic form
- reusable (the same training content can be used for overlapping needs for different cadres)
- easily updatable (to allow easy change of standardized content)
This component is built to include all stakeholders that delevelop training material, ranging from national institutions, technical and programmatic experts, to instructional learning experts and digital media creators. They all need to follow uniform processes to interact and produce training material, spanning all of NTEP operations, in a consistent manner, maintaining a high level of quality.
The system of content development will be made of three parts, the Knowledge map, the Page Library and Training Courses and curricula.
1. The Knowledge Map:
The entire universe of ideas/ concepts required for training in NTEP has been visualized as a map called the ‘Knowledge map’. Each unique idea/unit in the Knowledge Map is called a ‘node’, which serves as a building block to the entire training content development process.
2. The Page Library:
For each node on the knowledge map, standardized training content is built as a Page. A page is expected to impart training related to the learning objectives defined on its knowlege node, in a maximum duration 3 mins. While developing the page, questions related to the learning objective are also defined. Each page is translated into necessary language versions. Pages for all the knowledge map nodes are available in the “Page Library".
Development of pages will include:
- Understanding learning objectives and gathering technical material
- Designing/ redesigning the instruction/ digital content for each page using various media (Text+/- images, Audio/ Videos, interactive animations etc) based on feedback from the end-users.
- framing questions associated to the various learning objectives and adding them along with the page
- translation of select pages according to need/feedback from the end-users
3. Course/ Curriculum Development:
Pages drawn from the Page library will serve as building blocks for designing training curriculum or “Courses”. Any number of Courses can be prepared by grouping/ structuring the pages from the Page Library in a sequence. The grouping/ selection of various pages and their sequencing will address all varieties of training needs for different cadres. Pages are organized under chapters in a sequence; chapters are in turn organized under modules and later modules are organized into Courses. Courses will be used to implement training.
This model where the training content development is divided into three parts, allows adherence to the initial principles of reusability, standardization and ability to be kept updated. Through the knowledge map there is a comprehensive understanding of the various current knowledge/ training needed in NTEP and becomes a repository of the same. The content in pages is standardized for use across the country. The availability of individual pages allows it to be reused in multiple training courses for different cadres; and allows individual pages to be updated, whereby the courses using these pages can be automatically updated with the latest information or upgraded into a more engaging and prioritised way.
The Pre-test , intermediate quizzes and post-test also constitute an important component of the course curriculum. These quizzes are composed of selected questions drawn from the question bank generated from the pool of questions linked to each page added to the course.
The processes related to all the three components described above are carried out in the online tool built for this subsystem called the Knowledge Base.
1.1 The Knowledge Map
1.1 The Knowledge MapThe first component of the Knowledge Base is a map of all ideas that need to be imparted to a trainee in NTEP. This section describes the various concepts, principles, roles and processes related to maintaining and updating the knowledge map.
Concepts
-
KMNodes(Knowledge Map Nodes) :
A KMnode may be a unique concept, process, idea, definition, algorithm, or any other aspect with a specified learning objective.
-
Relationships:
The KMnode will have defined relationships with other KMnodes which may further detail or explain the concepts or describe a higher-level concept.
For example, there will be a node defined for the concept of ‘ZN microscopy’ and it will be related to further nodes such as ‘staining’, ‘smear preparation’ and so on, or link ZN microscopy and Fluorescent microscopy through the overall concept of ‘Microscopy’ in general. Thus, the nodes and their relationship will exist as a network / map where there is no defined hierarchy. The hierarchy will dynamically be identified when a trainee or training need is defined.
The KMnodes have the following attributes:
Table 2: List of Attributes of the KMnode
| Attribute | Description |
| ID | This is a unique identifier for tracking the nodes in the knowledge map database. |
| Name | Title of the page. This should be able to identify the unit sufficiently and its difference to other pages should be clearly evident. |
| Description/ Learning Objective | Provides short synopsis of what the content associated with the unit should cover. |
| Maintainer | Name/ UserName of the expert who is currently responsible for the maintenance of the node and its related training content. The maintainer has to ensure that the node and its content are in line with the principles of the knowledge map and with the current guidelines/ directives. |
| Relationships |
Describes the relationships of the node to other entities. This will include entities such as
|
The current version of the Knowledge Map can be viewed from the link. The knowledge map here is represented as a list of nodes linked with other units in the knowledge map.
Principles of the knowledge map
- Idea/ concept centric- Non audience dependent: The KMnodes and their learning objectives linked to it represent one defined idea/ concept.
- Unique Unit Based: A learning objective will only be represented in one and only one node.
- Complexity in division: In cases where the concept or topic to be discussed has many aspects, a single node may be used to represent the overall concept in brief, while specific details or in depth concepts may be presented in other nodes.
- Dynamicity, Organic and iterative evolution: The knowledge map is meant to be a dynamic collection of nodes, where new nodes are constantly added with new program areas/ expansion, older nodes updated with changes in program structure and deleted with outdated concepts/ideas being removed. These changes are to be made in real time as and when the program update/ change happens.
Roles
- Maintainer: The maintainer is a person/ expert who is responsible for maintaining the integrity, comprehensiveness and quality of the knowledge map and ensuring adherence to the above described principles. The maintainer may perform additions, modifications, and depreciations(Deletions) of nodes on the knowledge map. There may be many maintainers organized into a committee/ group and may be collectively responsible for the knowledge map. Each maintainer may be assigned a group of nodes to maintain. All nodes will mandatorily need to be assigned to a maintainer.
- Content Creator: Content creators are people who develop training content for each KMnode on the knowledge map. A content creator may be assigned a node to develop content against. However, they only have view permissions on the knowledge map; but may be able to respond to comments made by anyone on the nodes assigned to them.
- Others: The knowledge map being open content, all users(including the above two) may have access to view the entire knowledge map. They may suggest new nodes on the knowledge map and add comments/ suggestions on existing nodes. New nodes will need to be approved by the assigned maintainer before it is published on the knowledge map. Each newly added node will also be assigned to any one of the maintainers.
Processes
- Add new node:
- Submit draft node: Any visitor on the knowledge map may suggest addition of a new node. New nodes need to be linked to any one existing “Parent” node and will be first added in a Draft mode. The maintainer of the parent node will be assigned to the new node. The visitor adding the node needs to fill in all the attributes of the nodes mandatorily.
- Review by Maintainer: New nodes added in Draft mode will be notified to the Maintainer, who will review the node and will perform the following actions
- Approve the new addition after it passes the following checklist. If the node does not pass it; the maintainer may outright reject the draft node or modify the attributes till it passess the checklist.
- The name of the node and the learning objective are clear and precise. For example, “Burden” is an unclear title; while “Burden of TB in India” is clear and precise.
- There are no other nodes in the knowledge map with overlap/ have duplicate learning objectives with the new node added.
- There is a training need that is attributable to the new node. For, example; in NTEP training, “Manufacture of 3FDC” may be considered as out of scope of training.
- Assign a different maintainer. The existing maintainer may judge that the node is better dealt with by a different maintainer, he/she may assign it to a different maintainer in the maintainers group.
- Approve the new addition after it passes the following checklist. If the node does not pass it; the maintainer may outright reject the draft node or modify the attributes till it passess the checklist.
- Publish the node: Approved new nodes get published on the knowledge map.
- Submit draft node: Any visitor on the knowledge map may suggest addition of a new node. New nodes need to be linked to any one existing “Parent” node and will be first added in a Draft mode. The maintainer of the parent node will be assigned to the new node. The visitor adding the node needs to fill in all the attributes of the nodes mandatorily.
- Update existing node:
- Maintainers of the node may update any of its attributes except the unique identifier. All changes to a node will be tracked as different versions of the node. The update may be performed for the reasons such as:
- Update in Name/ Learning objective: The update may be triggered by various needs/ events, such as change in policy/ guidelines; any error identified on the learning objective or better understanding of the purpose of the node.
- Adding/ changing node relationships: The maintainer may identify new connections with existing nodes on the knowledge map.
- Re-assigning maintainers: The existing maintainer may assign a node to any other maintainer on the maintainers group.
- Maintainers of the node may update any of its attributes except the unique identifier. All changes to a node will be tracked as different versions of the node. The update may be performed for the reasons such as:
- Depreciate existing node: Any existing node may be depreciated when the node/ learning objective becomes outdated or no longer relevant. Such depreciated nodes effectively get removed from the published knowledge map.
- Commenting/ Discussions: Any visitor on the knowledge map may comment/ provide suggestions on any of the existing nodes. Comments may be reviewed/ replied to by the node maintainer/ the content creator assigned to that node.
1.2 Content Development
1.2 Content DevelopmentConcepts
-
Content Page:
A Content Page is a unit of training content that expresses the learning objectives on a KMnode on the Knowledge map. There will be one page of training content for every KMnode in the knowledge map. The content on each page is based on technical training material / SOPs / guidelines of NTEP and may explain or demonstrate it in more detail. In addition to the training material itself, the Content Page will also have certain additional details/ materials such as
- references to source documents or other credits/ acknowledgements
- attachments
- quick reference/ job aids/ posters
- raw editable versions of images/ graphics/ videos used in the main content.
-
Page Types:
Based on the type of material that is used on the Content Page, it is classified into various types. The list below is ordered in ascending based on the level of effort needed to create the page.
- Basic Page: These are pages that are built using simple text and images. The text and images may be based on content available in any existing guidelines/ documents/ training material, as per the needs of the learning objective on the linked KMnode. The Basic page should at least serve the needs of training delivered in an instructor led mode.
- Improved Basic Page: Basic Pages may be redone, to explain the concept in a better way using better graphics/ text, either by changing the way of representation (infographics), or by including examples / cases etc. This would improve the ability of the page to deliver the learning objectives to a level such that the trainee may read and understand the concept without any instructor.
- Video Lecture: This type includes where the content is a video of an expert explaining the concept in his/her own words in alignment with the learning objective. The delivery of the training will rely on the expert's ability to present the content in an easily understandable way. The video may use a slide deck with a video inset of the presenter, or a writing board/ background image along with the presenter. The voice of the presenter may be scripted and subtitled along with the video.
- Animation: These are pages with simple animated content in a video format. This page type may be used in cases where learning objectives may be delivered better using a schematic/ moving representation of the concept as opposed to other ones. For example, simple workflows involving different locations and people over time. This type excludes animations that can be created easily by tools such as power point and recorded as a video, and is meant to classify animations that require a professional animator to create it and is often commissioned. The content creation involves multiple stages such as scripting, key frame/ scene review, draft review, and final review and approval.
- Video Demos: These pages contain content that are video shots of actual locations where a procedure or a protocol is demonstrated. Here too the content creation involves multiple stages such as scripting, casting, field shooting, editing, draft production review, and final review.
- Interaction and Games : These are pages with many different types of user interactions, such as clicking, drag & drop, text entry and so on. It uses a combination of different types of raw material to achieve a learning objective including videos/ animations/ demonstrations and narration as needed. The interaction may require the user to apply the knowledge obtained to achieve and reinforce the learning objective. It may have one start point, but may branch out into different scenarios based on user interaction, with many end-points that may backtrack and re-join at different places. This page type may be used when the learning objectives are complex, with decisions/ judgements that need to be made. For example constituting a DR-TB Drug regimen for a given diagnostic scenario. The content creation involves multiple stages such as concept scenario design, scripting, key frame/ scene review, interaction testing, and final review
In cases where combinations of types are included in a page, the more complex type will be considered; for example, a video recording of an expert with an animation will be classified as an Animation.
The page may undergo evolution / upgradation with time based on changes in the program or based on need for better content representation. The page types will assist the upgradation process. The Basic Page type is the most easiest to create and is often the first created type. Based on the material on the Basic Page, which ensures basic technical accuracy of the training content, future upgraded versions of the page may be created.
-
Question
Based on learning objectives of a page and the training content placed in it, one or more questions may be added/ linked to the page. These will serve to assess whether a trainee has acquired the necessary knowledge/ understanding expected. The questions will usually be of multiple-choice type.
Principles
The broad principles that have to be followed while developing a page are as follows:
- Self contained/ independent: The training content on a page should be self contained and should not be built on the context of content available on any other page or continue from another page.
- Specific to learning objectives: The page should be able to deliver the learning objective without having to refer to another page and should contain only content specific to the learning objective of the knowledge map node linked to the page. There should not be any content included for the purposes of introduction or conclusion.
- As simple as possible: It should be possible to use any page for the training of any personnel. Hence the technical content should be explained in simple language as far as possible.
- Delivered in 2-3 minutes: It should be possible for the average trainee to consume the training content present on a page in 2-3 minutes.
Roles
- Content Creator: These are personnel that will create content against the Knowledge Map node assigned to them.
- Maintainer: The maintainer for a page is the same as the maintainer for the corresponding knowledge map node. The maintainer reviews and approves pages before it is to be published. He/she also is responsible for deciding the page type to be used while upgrading the page to a higher level page.
- Trainees: All users are by default Trainees. Trainees access the page through one or the other training curriculum. They may provide feedback at the level of a page through the comments on the corresponding linked knowledge map node.
Processes
Note: Upgradation and Modification of a page will be considered as a new version of the same page, with the same unique identifier. Older versions of the page may be available at the back end of the LMS and may be accessed on special demand.
- Creation:
- The content creator assigned to a knowledge map node will create the corresponding page and its content. He/She may interact with the Maintainer to identify learning objectives, source documents as required and prepare the training content before creating the page. On page creation the status of the page will be “Pending Review”
- Pages that are of the status “Pending Review” will be evaluated by the maintainer of the page/ corresponding knowledge map node. The maintainer may approve or reject pages based on whether it clears the following checklist
- Alignment of titles- The page title and the corresponding knowledge map node should have the exact same title.
- Specificity of content: The page content needs to be specific to the title and the learning objectives of the corresponding linked knowledge map node. It should not convey any message that is or may be represented in another page.
- Content independence: The content developed on the page should not be in the context of any other page and it should convey the learning objective completely.
- Simplicity: Generally any learned reader should be able to read and understand/ consume the content and its learning objective without additional reference/ reading.
- Duration: It should be possible to consume the content by an average reader within approximately three minutes. In exceptional cases it can be longer.
- Questions
- If the page does not pass the above checklist and is rejected by the maintainer then it will be converted to the stage “Pending Modification”. It will be passed back to the content creator for addressing the comments/ reason for rejection.
- The page will also need to be marked as “Pending Modification” once the corresponding KM Node (Title or learning objective) is updated.
- Modification: Pages that are with the status “Pending Modification” may be reviewed by the content creator and he/she may make changes as per the requirement/ comments.
- Upgradation: A page whose content has not been performing as well as expected and there is a scope to improve the delivery of the learning objectives by using another type of page, it may be tagged for upgradation. Once a page has been tagged for upgradation it will be available to the content creator in an upgradation queue.
- Translation: Certain pages after being built into courses for specific cadres who are less likely to understand English, may be tagged for translation into another regional/ local language. Once it is tagged for translation it will be available to the content creator in the Translation queue.
- Deletion: Page deletion only occurs when the corresponding KM node is depreciated. Such deletions may also be available on the LMS backend, but are not available for viewing.
- Prioritization: Individual pages depending upon the need to make available the published version it will have a certain priority value. Priority value of 10 means highest priority for content development, while 0 means least or no priority. The content creator may pick up pages from a queue for modification/ translation based on the order of priority. The maintainer of the page has the rights to set the priority of the page.
1.3 Curriculum Development
1.3 Curriculum DevelopmentConcepts
-
Course: A course is an organized sequence of sessions containing Pages, demonstrations, practicals, field visits, role plays, quizzes, Pre-test and Post-tests, which will be used for the training related to the program. A course is always specific to a cadre of staff, with a define role and specified competencies under the programme. A course should comprehensively cover all training requirements of that cadre.
Each course will have pages organized under the Page ---> Chapter ---> Module structure. Different courses will have different pages, but they may also use the same page as per the requirement of the course (which is linked with the same knowledge unit or node, and hence based on the same training need). This is depicted in the following schema:
Fig: Course structure
Each course will have a number of attributes as outlined below.
Course ID This is the unique identifier assigned to the course at the time of creation. Title: The course will be named according to the cadre it is intended to train. Eg. Course for Treatment Supporters on NTEP Course Description This is a short description of the course, which will outline the objectives of the course and the topics covered under it. CourseStructure The course structure will contain the data regarding the linkage of the various pages organized under chapters/ Modules and the corresponding quizzes at various stages within the course/ Module/Chapter. Intended Cadre This will indicate the various cadres eligible to take the course. Status This will indicate the status of the course in terms of whether it is in draft stage/ unpublished or published status. It may also include statuses such as depreciated. CourseMaintainer This is the person assigned to this course as the maintainer. -
Module: A module is created for a specific knowledge / functional area which is to be covered for a cadre based on the course objectives. A course may have different modules (knowledge areas) with different pages. For example, in the course for a Lab Technician, “ZN microscopy” may be a module.
NOTE: Modules may also have independent existence outside a course as well. These may be used for imparting a new knowledge area as a part of new expansion in the program or may be used for re/update training.
- Chapter: Chapters will be the topics that are to be covered under knowledge areas (modules). As above, there may be different topics (chapters) under each knowledge area (module). For example, in the module on Microscopy, “staining using ZN technique” may be one of the chapters. Chapters will hold the standardized learning material in the form of pages.
- Quiz: Courses will have quizzes at various stages (pre / post at the level of either course, module or chapter). The quizzes are created/ drawn from the questions attached to the pages that are contained within the course/ module/ chapter. The quiz, depending on how it is set up, will randomly draw questions from a set of questions that were associated with the pages. Based on configuration set by the course creator, the learners must pass/ clear the quiz to proceed and eventually complete the course and earn the certificate. The number of questions in an assessment and passing marks for each assessment will be set at the time of configuring the course/ module as per the need of the training. In the future a quiz may also be manually assessed/ scored.
- Certificate: Each course / module at the end or at achieving completion of the post-test successfully will have a certificate. The certificate is awarded from NTEP, and / or relevant institutions / stakeholders. A sample certificate has been provided in the Annex.
- Webinar: a webinar or an online training session would be scheduled inside the course whenever a remote facilitator would interact with the trainees for any particular purpose inside the course. This could be to deliver an instructor led session, conduct discussions or clarify queries.
Principles
The broad principles to be followed while creating a curriculum/ course are as follows.
- One cadre One course- At a time in the training system of NTEP a specific cadre/ designation will only have one active standard course. A course should be comprehensive, such that it allows all necessary content required to successfully execute the TOR/JD of the corresponding cadre. The monitoring of the training status of a trainee will be considered as Trained/ Untrained under his/her cadre based on whether he/she has successfully completed the single course for that cadre. The individual may undergo modules that are independently available outside his/her course and will count as additional credit.
- Logical flow in sequencing of content: The training content will have to be placed in a sequence within the course. The pages will be sequenced within a chapter, followed by Chapters into Modules and finally modules into Courses. This sequence depending upon the intended audience/ cadre will have to be selected and ordered to ensure that both the appropriate high level concept is introduced and necessary in depth concepts are also discussed afterwards.
- Inbuilt pre/ post test : All courses should have an inbuilt assessment mechanism to objectively identify whether he/she has completed the requirements/ gained all necessary knowledge and skills expected from the course.
- Standard schedule: The course may be executed/ operationalized as per the convenience of the institution; however a standard scheduling pattern may be set.
Roles
- Content creator - The content creator(described above) will also double up as the course creator/ curriculum designer. They will select and organize the pages prepared into chapters> modules> Courses in a sequence appropriate to the cadre. The content creator can create the course in unpublished form.
- Maintainer - The maintainer may review the draft/ unpublished courses and publish them. They may also unpublish existing courses and send them for revisions to the content creator or depreciate them altogether.
- Operational Roles
- Course Coordinator - The course co-ordinator at various states/ STDCs will schedule the various courses according to the plan and training needs of the state and coordinate the conduct of the course
- Trainee - The trainee may access the course if he/she is one of the cadres for which the course is listed
- Facilitator - Facilitators may access the course when it is scheduled and he/she is added to that schedule as a facilitator.
Processes
- Create a new course: Once pages are available, a content creator may organize the pages into a course. After the Type A0 page is approved and published on the CTD e-learning platform, it may be included into a course.
- Review and Approval of the course: Once the course is configured, approval from CTD and other stakeholders will be sought. A meeting of relevant stakeholders will be called to discuss feedback and will be documented. Relevant changes will be listed and made by course creator,
- Set up the course evaluation: As described in the previous section a course will have pre / post evaluation at the level of either course, module or chapter, randomly drawn from the questions attached to the pages that are contained within. The number of questions in an assessment and passing marks for each assessment will be set as per the need of the training in consultation with the relevant stakeholders.
- Configure the course certificate: A certificate for successful completion of the course will be awarded to the participants based on their performance in the course evaluation. The certificate will be designed with appropriate logos of the awarding organizations and will be decided based on consultation with the relevant stakeholders. A sample certificate is provided in the Annex for reference.
- Setup the feedback form: two types of feedback for a course will be sought from the facilitators and trainees:
- Performance or retention of knowledge / skills from the course / module.
- Qualitative and Quantitative feedback from the end users on various aspects of the course/ module.
- Scheduling the course: Generally, once a course is configured, it needs to be scheduled for it to be accessible to trainees. Scheduling a course involves setting the start and end date for the course, adding webinars, contact sessions/ evaluations, adding facilitators, enrolling participants etc. The scheduling is done by the course coordinator based on the training plan.
Style Guide
Style GuideThe style guide provide reference to what standard styles should be used while developing content. This would ensure uniformity of content appearance and will ensure that the trainee would identify the content as belonging to a whole. The style guide would specify standard content styles that can be applied to online content. This would include the following. ( Click the item to read more.)
- Formatting Guide - (Note: Work in Progress)
- Basic Color Palette
- Text (Headings, Bullets and numbering, Quotes, Captions)
- Tables
- Images(Pictures/ photographs/Graphics)
- Library of standard graphics
- Videos and Animations
- Language Guide (TB inclusive Language)
Formatting Guide
Formatting GuideEnsuring consistency and professionalism in the content on the platform is crucial for an effective learning experience. Adhering to specific formatting guidelines helps maintain clarity and coherence in the content.
File Location: Search for specific course materials or content pages within knowledge base platform. It involves navigating through various parameters or criteria to pinpoint the desired information. In the context of our platform, locating a file entails searching for a particular content page based on factors such as page ID, title, status, creator ID, or tags.
- Page Library: The Page Library provides a means to locate files based on various parameters, including status (published on LMS, approved, final review etc.), page tags (content overload, for upgrade, grammar check etc.) , page ID, content creator ID, and title, among others. Users can input any combination of these parameters to find the desired content page. Access to the Page Library is available through the provided link- https://ntep.in/PageLibrary .
- Knowledge Map: To access files, users can search for the content page title within the Knowledge Map. They can then refine their search based on the status of nodes (pending review, live, depreciated), if needed. Utilize the provided link- https://ntep.in/km-nodes to navigate to the Knowledge Map.
- Curriculum: Access the approved courses as well as those under development by navigating through the provided link- https://ntep.in/curriculum?field_grouptype_target_id=40 . This link grants access to a variety of content pages associated with these courses, including nodes and sub-nodes.
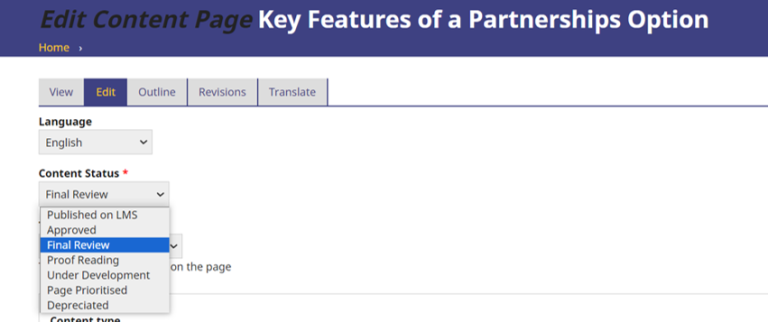
After identifying the desired content page, attention should be given to several parameters including content status, content type, page tags, content creator, and revision information. Before proceeding to translate HTML content to H5P or modify existing H5P content, it is crucial to ensure the correct content status is selected.
Further details on other parameters will be provided after explaining the content type.
Content Type (Course Presentations): H5P offers diverse content types catering to various interactive needs, facilitating easy creation of engaging materials. For detailed information, refer to https://h5p.org/content-types-and-applications. Our focus here is on course presentations, where we'll create interactive slides to enhance engagement and learning.
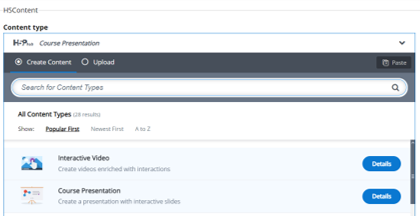
Ensure that the HTML content utilizes course presentations, with each presentation containing a maximum of 7 slides. If accordion or column formats have been used previously, maintain them without making any alterations.
Below is a thorough guide to assist you in creating or editing content pages while ensuring they meet the required standards:
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|
1. |
Font Size |
Content title: 100% (Bold) Image
Image
|
|
2. |
Margin |
1 cm (as indicated by the red lines in the content page provided) Image
|
|
3. |
Color Scheme |
Blue (sharp blue), orange (carrot) or green (emerald green) Image

|
|
4. |
Videos |
Download the videos embedded within the HTML content and then upload them onto the course presentation for integration. Image
Image
|
|
5. |
Infographic |
Image

Image
For new infographics, if the text isn't clear on existing figures, utilize templates available at https://www.presentationgo.com/ . Upload only the image of the template (e.g., triangle, hexagon) to the H5P software. Add text separately on H5P after uploading the template image. Image
Note: |
|
6. |
Icons |
You have the option to use https://www.flaticon.com/ for icons. Additionally, you can employ separators like horizontal or vertical lines to distinguish content text from the icons. Image

|
Language Guide
Language GuideThe Language guide is primarily extracted from the 'Words Matter' document (Second Edition published by StopTB Partnership in 2022, https://conf2022.theunion.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/stbp_words-mat…). Its use has been envisioned to guide the accommodation of inclusive language for TB training & communication while developing & reviewing course content under the Modernised Training System. Categorized into 'Alternatives', 'To be Carefully Used' and 'Emerging Terms', the guide underlines terms that 'must be replaced or alternatives that are sensitive and inclusive, use of terms that must be re-considered and other emerging terms in TB.
Alternatives
|
Use |
Replace |
Comments |
| They/them | He/him, She/her | More inclusive & gender sensitive |
| Contact Person | TB Contact | Does not have strong negative connotations but is not person-centered |
| Person Lost to Follow Up | Defaulter | Unnecessarily and unfairly places blame on the person receiving treatment |
| Noncitizen resident or Unauthorized resident/worker | Illegal/Alien worker | Offensive & isolates their access to TB treatment & care |
| Person with presumed TB | TB Suspect | Negative association |
| TB Prevention & Care or Ending TB | TB Control | Its continued use is no longer recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) not people-centered, ignores contributions of communities & people affected by TB, -ve connotations of TB authorities as being in full control of all aspects of prevention, treatment & care |
| PLHIV/AIDS PLHWA/Person living with HIV | AIDS Patient | Necessary to reflect the fact that an HIV-positive person may continue to live well and productively for many years |
| Person Living with HIV/AIDS | Innocent Victim | The term wrongly implies that people infected in other ways (other than those infected medically or at birth through no fault of their own) are somehow guilty. |
| Person/s with physical disability | physically challenged | The term ‘physically challenged’ is deemed inappropriate as it places focus on the identity rather than the person & their barriers |
To be carefully used
|
Use |
Use carefully |
Comments |
| Person with presumed TB | Presumed Presumptive | The term ‘Presumed Presumptive’ places emphasis on the disease and not the person with possible tuberculosis. While, it can be used to describe a stage in the process of diagnosing TB, when discussing an individual, it is best to say a person with presumed TB |
| Burden | It should be stressed that it is the disease, not the people affected by the disease, that burdens a country, a region or the world | |
| Case Finding/Case Detection | Activity occurs by virtue of action taken by the person experiencing symptoms | |
| People deprived of their liberty | Prisoner/Inmate | An alternative can be ‘People deprived of their liberty’ (in some contexts it can stigmatize people and can impact perceptions regarding the right to health for all |
| Compliance, Non-Compliance | Noncompliance unfairly assigns blame to the person receiving treatment when many external factors outside a person’s control may be the cause | |
| Adherent/Nonadherent | Unfairly assigns singular responsibility for treatment completion to the person receiving treatment, when many external factors outside a person’s control | |
| Mobile Worker | Refers to a large category of persons who may cross borders or move within their own country on a usually frequent and short-term basis for a variety of work-related reasons, without changing their primary residence or home base | |
| Bacteriologically +ve/-ve | Sputum/Smear Positive/Negative | Smear microscopy is no longer recognized as a recommended diagnostic strategy. The preferred term is bacteriologically positive/ negative |
| Key and Vulnerable Population | Risk Groups | While the term is used in the epidemiology of TB to describe clinical risk groups when discussing an individual or group, it is best to say key and vulnerable populations . |
| Person Affected by TB/Person on Treatment/Client | Patient/TB Patient | Patient/TB Patient ‘clinicalizes’ them and focuses on the treatment process rather than the person |
Emerging Terms
|
Terms |
Definition |
| COVID-19 | An infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. COVID-19 was first reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019 |
| Bi-Directional Testing | The delivery of simultaneous diagnostic testing for more than one disease |
| COVID-19 Response Mechanism (C19RM) | A special initiative of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, TB and Malaria to provide countries with additional funding to respond to COVID-19 to mitigate its impact on HIV, TB and malaria programs and to initiate and strengthen improvements in health and community systems |
Setting learning objectives
Setting learning objectivesThis document outlines the principles for stating learning objectives for each KM Node.
Following are the steps for defining learning objectives.
- Clearly outline the anticipated outcomes that learners will be able to demonstrate after engaging with each page.
- The learning objectives should be stated such that it correspond to these outcomes. It should guide what the content page should represent. Specify what learners will be able to do, ensuring that objectives:
- clearly defined or describes an action
- are measurable
- Ensure that objectives are learner-centric, focusing on the behaviors that learners should adopt after going through the content, rather than focusing on what the page will “teach”
- Incorporate action words from the Modified Bloom’s Taxonomy (see reference table below).
- Choose an action word from the various levels of objectives (Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, Evaluation) when formulating learning objectives, aligning them with the educational activity's overarching goal.
- Refrain from using vague terms like understand, learn, and know, as they lack measurability due to the absence of tangible outcomes.
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Measurable Verbs:
Benjamin Bloom devised a taxonomy of measurable verbs to facilitate the description and categorization of observable knowledge, skills, attitudes, behaviours, and abilities. This theory posits that there exist discernible levels of observable actions indicative of cognitive activity within the brain. Through the utilization of measurable verbs in crafting learning objectives, the explicit actions required to demonstrate learning are articulated.
Table 1: Measurable verbs
|
Category |
Meaning |
Verbs |
||
|
Knowledge |
Remember previously learned information. |
Arrange Choose Cite Define Describe Draw Enumerate Identify Indicate Label List
|
Locate Match Name Order Outline Quote Read Recall Recite Recognize Record
|
Relate Repeat Reproduce Review Select State Study Tabulate Tally Tell Underline Write |
|
Comprehension |
Demonstrate an understanding of the facts. |
Articulate Associate Characterize Clarify Classify Compare Compute Contrast Convert Defend Describe Differentiate Discuss Distinguish Estimate Example |
Explain Express Extend Extrapolate Factor Generalize Give Give examples Identify Illustrate Indicate Infer Interpolate Interpret Locate Match Observe |
Organize Paraphrase Predict Recognise Relate Report Represent Restate Review Rewrite Select Summarize Tell Translate
|
|
Application |
Apply knowledge to actual situations. |
Acquire Act Adapt Apply Ascertain Assign Avoid Back Back up Calculate Capture Change Chart Choose Classify Complete Compute Construct Consult Convey Customise |
Demonstrate Develop Discover Dramatize Derive Employ Experiment Explain Execute Generalize Guide Identify Illustrate Implement Interpret Interview Manipulate Modify Obtain Operate Organize |
Paint Perform Practice Predict Prepare Produce Process Provide Relate Schedule Select Show Simulate Sketch Solve Translate Use Utilize Write |
|
Analysis |
Break down objects or ideas into simpler parts and find evidence to support generalizations. |
Administer Analyze Appraise Break Break down Calculate Categorize Chart Classify Compare Conclude Confirm Contrast Correlate Corroborate criticize Identify Illustrate Infer Inspect Debate |
Deduce Delegate Detect Diagnose Diagram Differentiate Discover Discriminate Dissect Distinguish Divide Document Ensure Establish evaluate Examine Experiment Figure Group Inventory Investigate |
Manage Monitor Order organize Outline Point out Predict Prioritize Question Reconcile Relate Resolve Select Separate Solve Subdivide Survey Test Transform Troubleshoot |
|
Synthesis |
Compile component ideas into a new whole or propose alternative solutions. |
Anticipate Appraise Argue Arrange Assemble Assess Brief Attach Choose Collect Compare Compile Conclude Consolidate Construct Contrast Core Counsel Create Criticize Critique Decide
|
Defend Describe Depict Design Develop Determine Discriminate Enhance Estimate Evaluate Explain Facilitate Formulate Frame Generate Grade Handle Invent Judge Manage Mediate Modify
|
Organise Prepare Prescribe Probe Propose Rate Rearrange Reconcile Refer Relate Release Reorganise Revise Rewrite Select Set up Specify Supervise Synthesize Test Value Verify Weigh |
|
Evaluation |
Make and defend judgments based on internal evidence or external criteria. |
Appraise Argue Arrange Assemble Assess Categorize Choose Collect Combine Compare Compile Compose Conclude Construct Create Design Develop Devise Estimate Evaluate
|
Explain Facilitate Formulate Generalize Generate Hypothesize Improve Integrate Invent Judge Justify Make Manage Measure Modify Organize Originate Plan Predict Prepare
|
Produce Propose Rate Rearrange Reconstruct Relate Reorganize Revise Rewrite Role-play Score Select Set up Specify Summarize Support Synthesize Tell Tell why Value Write |
Subsystem 2: Training Operations
Subsystem 2: Training OperationsThe activity of the actual conduct of Training is addressed in the Subsystem 2: Training Operations. It deals with the actual activities of planning, resourcing and conduct of Training, building on the outputs of Subsystem 1.
This subsystem is assisted in all processes using an online tool called the Learning Management System (LMS). The LMS serves as a platform where various stakeholders such as training coordinators, facilitators and trainees interact with each other to manage and complete the various training processes. There are many LMSs available, such as Swasth-eGurukul, iGOT, SAKSHAM; and any of them may be used for training as prescribed in the trainer's guide.
Training operations have the following steps.
- Making the Course available on the LMS (prior-requirement)
- Planning cadre-wise training at the individual level, Scheduling Training
- Conducting Training
- Monitoring and Reporting Training
Training Operations are further discussed in detail according to the following headings.
- Concepts
- Step 0: Making the Course available on the LMS
- Guide for Course-coordinator on LMS
- Guide for Trainers on LMS
- Guide for Trainee on LMS
- Step 1: Training Planning and Scheduling
- Step 2: Conducting the Training
- Step 3: Reporting of Training
2.1 Roles and Responsibilities of key Stakeholders
2.1 Roles and Responsibilities of key StakeholdersRoles and responsibilities of Key Institutions are as following:
| Institution | Activity |
|---|---|
| State TB Office (STO) |
|
| State TB Training & Demonstration Center (STDC) |
|
|
District TB Office |
|
Roles and responsibilities of Key Personnel are as following:
|
Sr |
Personnel |
Activity |
|
1 |
Training Coordinator (STDC) |
|
|
2 |
Master Trainer - For designated cadres |
|
|
3 |
Trainer - For designated cadres |
|
|
4 |
Program Managers (STO, DTO,) |
Competency assessment and assign staff for re-training |
2.2 Learning Management System
2.2 Learning Management SystemLearning Management System (LMS) is an IT Application which can be accessed via a computer or mobile device. Swasth-eGurukul is a LMS created by ‘World Health Organisation’ (www.swasth-egurukul.in). LMS enables effective management of large-scale training programs involving a large number of trainers and trainees. LMS could aid in the following activities. The key User roles in LMS are:
|
Sr. |
User Role |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Course Coordinator |
|
|
2 |
Trainer |
|
|
3 |
Trainee |
|
2.3 Training Planning (by STDC)
2.3 Training Planning (by STDC)- Budgeting, PIP, Training calendar, infra
- States will have to have a designated a Course Coordinator at the STDC
This section is being elaborated. Please check back later for details.
2.4 Conducting the Training for each planned batch
2.4 Conducting the Training for each planned batchFollowing is a set of activities which need to be taken up by the various stakeholders to plan and execute the training:
|
Sr. |
Activity |
Activity Type |
To be done by |
To be done when |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Collect information about trainees |
Once per batch |
Course Coordinator |
Planning stage |
Use format provided in Planning Tool To coordinate with DTOs |
|
2 |
Identification of resources required for training |
Once per batch |
Course Coordinator |
Planning stage |
Training location, stay, food etc. to be identified in close coordination with STDC/ STC/ Districts |
|
3 |
Batch Creation |
Once per batch |
Course Coordinator |
Planning stage |
Use format provided in planning tool to create batches and assign trainees |
|
4 |
Scheduling the Course |
Once per batch |
Course Coordinator |
Planning stage |
Course coordinator needs to schedule the course as per the sanctioned/approved training plan/calendar. The necessary events in the training schedule(Webinar, virtual sessions, in-person sessions, demonstrations, training evaluations) should be decided at this stage. |
|
5 |
Communication/ Invitation to Trainees |
Once per batch |
STDC/DTO |
When the training is scheduled on the LMS |
STDC/STC can direct the DTOs/incharge to relieve the trainees for the training |
|
6 |
Registration of Trainees on LMS |
Once for each trainee |
Trainee |
Before any training on LMS |
The trainees should register on LMS and fill in the necessary details. The trainees who’ve already registered can use their existing login credentials for enrollment. |
|
7 |
Enrollment of Trainees for the Course |
Once for each course |
Trainee |
Once a course is scheduled on LMS |
The trainees need to enroll for the course that has been scheduled on LMS |
|
8 |
Admitting Trainees to the Course |
Once a day/ on Need basis |
Course coordinator |
Before training starts |
The course coordinators may admit the trainees |
|
9 |
Pre-Test |
Once per course |
Trainee |
Before Training starts |
The trainees should complete the Pre-test before starting the training. |
|
10 |
Training Delivery |
Once per course |
Trainer |
During Training |
The trainer/ facilitator should deliver the training as described in Chapter wise trainer’s guide. |
|
11 |
Post- Test |
Once per course |
Trainee |
After Training |
The trainees should complete the post-test at the end of training.Passing of the post-test is mandatory for the successful completion of the training |
|
12 |
Certification |
Once per course |
Trainee |
After Training |
Based on the performance of the trainee in the interim quizzes and post-test, a certificate is generated for the course |
|
13 |
Analysis and Reporting |
Once per batch |
Course coordinator |
Within 1 week of end of training |
2.5 The Planning tool
2.5 The Planning tool
The excel based Planning tool (Ref: Annexure) will be used primarily for the following activities:
|
Sr. |
Activity |
Sheet Name |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Collection of Trainee information (Name, Designation, District/TU/PHI, phone no, email ID, LMS details etc. |
Trainee Database |
|
2 |
Create Batches as per the resources available - specify no. of Trainees, training location, training dates, mode of training and Trainers’ details |
Training Batch |
|
3 |
Assign Trainees to the various Batches |
Trainee Database |
The Training Planning Tool can be downloaded from this link:
2.6 Training Prerequisites
2.6 Training PrerequisitesFor ensuring seamless and effective training, the trainers and trainees need to ensure that they adhere to the following prerequisites. This section lists down the prerequisites for the trainer and trainee for conducting the training.
- Trainer
- Attend and complete the Training of Trainers (TOT) for the Course
- Register as a trainer for the course in NTEP/ STDC (in Swasth-eGurukul).
- Thorough with the latest version of the Trainers’ guide available online.
- Well-acquainted with the training processes to be followed for conducting training in Swasth - eGurukul.
- Have access to the Course on Swasth-eGurukul
- Have access to the participant list and the schedule of training on Swasth-eGurukul
- Ensure that the necessary arrangements for demonstration are in place (such as equipment, NTEP physical forms, Login credentials of Nikshay/ Nikshay Aushadhi, etc.)
- Have access to a computer or Laptop and good internet connection
-
Trainee
- Have access to a device (laptop, Tablet or Mobile) with good internet connection.
- Register on Swasth-eGurukul as a trainee.
- Enrol for the course (once the Course has been scheduled)
- Attempted the Pre-Test before the training
2.7 Training Monitoring
2.7 Training MonitoringTo successfully conduct training at a large scale, close monitoring is critical and LMS enables the administrators to track the progress. As the trainees across the country register themselves in the portal, LMS would eventually have the database of the trainees trained in NTEP. Since training would be a continuous activity, this database would be updated as and when training is conducted. As the trainees would need to register for courses and go through the content and assessments using LMS, the system would know trainee wise - course wise - training status including the dates of the training and their performances in various assessments. This information would help the Program Managers in planning the refresher training. Analysis of the assessment scores would help the Program Managers understand the training needs of the staff. Based on the analysis, focussed training sessions on specific topics (which are less understood) could be conducted.
Training Modes
Training ModesMode of Training may be described in terms of two aspects, physical presence and the role of the instructor.
- Role of instructor
- Instructor-led learning - The trainer, using the standardized content available, explains the concepts mentioned therein. They will emphasize the necessary aspects and may demonstrate the processes/ equipment.
- Self-learning - Trainees using the standardized content may read/ consume it and learn the related concept.
- Physical Presence
- Remote/ Virtual: The trainee attends the training and uses the content at their own locations.
- In-person: The trainees are present at a training venue in-person.
| Mode Of Training | Instructor-Led | Self-paced |
|---|---|---|
| Present in-person |
Classroom training led by a trainer |
Modular reading at the training centre |
| Present virtually |
Webinars by facilitators |
Remote, self-paced |
Blended training - Through the NTEP training System, a mix of the above two training aspects may be used to complete the training. Sessions that require hands-on training, especially in cases where demonstrations/ practical exercises are required, need to be conducted in an an instructor led physical mode, while basics and theoretical aspects may be left for remote self-paced learning. The blended approach would leverage the best of virtual/ in-person and instructor-led and self-learning. It would enable the program to make the best utilization of time, money, instructors, venue to give the best possible outcome.
Subsystem 3: Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation of training
Subsystem 3: Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation of trainingThis component provides guidance to program managers on how
- to monitor the status and performance of training
- to link up routine supervision of on ground activities and staff along with identification of training need
- to evaluate delivery of training in terms of quality and efficiency of processes.
This section is being expanded and updated.
Principles of Training Evaluation
Principles of Training EvaluationThe most widely used training evaluation method is the one provided by Donand Kirkpatric in 1959 & 1998 to assess the effects and impact of training programme at four different levels. These levels are arranged in the order of improvement in the desired work output by the individual due to training.
| Level | Component | Objective Measure |
|---|---|---|
| I | Reaction | Participants satisfaction |
| II | Learning | Change in knowledge, skills & attitudes of the participants |
| III | Behaviour | Measuring the behavioural change in the participant |
| IV | Results | Assessing the impact of the training |
Level-I Reaction Evaluation:
The assessment of immediate effect of the training programme that need to be evaluated during or immediately after the training session. This will be ensured by providing a session evaluation checklist after each session in the training. This can be implemented at two levels either orally or by written feedback. Immediately after each session separately or at the end of the day separately for each session / combined as per the objectives of the day’s schedule.
| Date & Time of the session: | |||||
| Topic / Title: | |||||
| Faculty: | |||||
| A. Objective evaluation: | Response | ||||
| Very poor | Poor | Average | Good | Very good | |
| 1. The topic was relevant to me | |||||
| 2. The topic was relevant to its contents | |||||
| 3.Appropriate knowledge of the facilitator/ presenter | |||||
| 4. Clarity in the facilitation/ presentation | |||||
| 5. The contents of the discussion/ presentation were appropriate | |||||
| 6. The contents were adequately covered | |||||
| 7. Participant interaction : Aroused interest of the participant | |||||
| 8. Participant interaction: Allowed participant questions | |||||
| B. Qualitative evaluation: | Response | ||||
| Enlist two best things of the session, you like most? |
|
||||
| Enlist two important things you suggest for improvement? | |||||
| C: Overall Evaluation: | Grade the overall performance of the presentation on 1-5 scale as above. | ||||
| Very poor (1) | Poor (2) | Average(3) | Good(4) | Very good(5) | |
Level-II Learning:
This type of evaluation is commonly performed by pre/post-test evaluation. A framed set of questions are put forth to the participants before they are exposed to any of the course content. This is pre-test evaluation. Pre-test evaluation provides valuable information about the status of knowledge and attitudes of the participants before attending the training programme. Then they are exposed to the training as per the schedule. At the end of the course again the same set of questions are provided to the participants and their scores are tallied to assess the performance of the training programme with respect to the knowledge and perception/attitudes of each of the participant.
Following is the checklist for pre/post-test evaluation of the training programme to assess the performance of the programme.
- The pre/post-test evaluation is to be done for assessment of the training programme and should never be viewed as the performance of the participant.
- The pre/post test questions should be alike and it should not differ, so as to evaluate the performance of individual trainee based on their performance before and after the training programme.
- The pre/post test questions should contain proportional representation of the course contents. Such questions can be derived from the curriculum contents as provided in the training design component of this document.
- The pre/post test questions should be in the form of multiple-choice questions (MCQ). These questions should be pretested and validated for quality and contents. Item analysis should be performed for the set of questions being used in the questionnaire.
- The pre/post test questions should be based on the contents taught in the session, however some logical interpretations out of the didactic sessions can be expected but number of such questions should be only a few.
The questions in the pre/post-test questionnaire need to be updated frequently. 10% revision of the questions according to the operational programme modifications being done time to time can be adjusted in the course contents as well as in the evaluation formats. Many times, it is felt that the participants should learn everything. Unfortunately, it is not possible to learn everything! Knowledge of human body and medicine, understanding of traditions and ways of behaving in a society, skills in administration and in educational methods are all relevant to health care staff. Learning all that is known in all of these fields would be beyond the scope of the most able student in the largest course. Therefore, the choice has to be made about what details should be left out of the course. It is simply not possible to learn everything that is known about medical sciences and health care. So, some selection is essential.
The content evaluation of any session needs to be designed based upon:
- Work profile of the participant in the implementation of the programme.
- The expected level of improvement from the participant
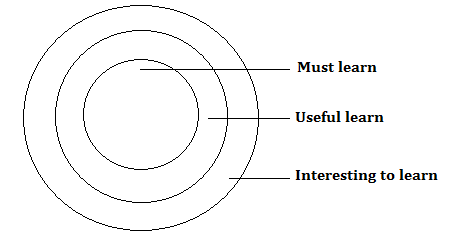
To fulfil the above needs the technical content evaluation sheet require to be covering the must know, desirable to know and nice to know topics in appropriate proportions.
The contents of any training session should address the need of the participants. 70% proportion of the content evaluation sheet should contain the basic programme expectation from the participant, which is the most important expected gain from the participant, desirable gain and nice to gain the knowledge need 20% and 10% proportion in the evaluation.
Level-III Behaviour:
To assess the behaviour, change in the participants of the training programme, they should be allowed to work in their specified location and position. The performance of the worker in the field after the training programme can also be assessed by an assessment questionnaire. Such evaluation should be preferably carried out after 6-12 months of the training programme. The behaviour change assessment can only be performed with the cooperation from the supervisor of the person to be evaluated. To avoid subjective bias in the assessment of the behaviour change in the training participant, supervisors of the trainee can be blinded by the exact questions of evaluation. But the assessment of effectiveness of the training programme should invariably include the supervisor’s perception about the individual’s performance before and after the training programme in a positive manner. Such evaluation can be performed based on several activities of the health personnel such as case finding activities, treatment compliance etc. Behavioural performance assessment can be done in two stages.
- Stage 1: Self-assessment of the performance: In this evaluation the individual is asked to assess his/her own performance with respect to contribution to various components of the programme. E.g., case finding, ensuring treatment compliance, stigma reduction in the community, patient education on DOT etc. This set of activities are pre designed into as per known enlisted components of the programme and individual contribution to these components.
- Stage 2. Assessment by the supervisor: The assessment of the performance of an individual with respect to the self-assessment of the contribution towards various programme components. To avoid subjective bias the performance of several other individuals (employees) also can be asked.
The common observations between the self-assessment and supervisor’s assessment are enlisted and graded for further evaluation. The pre and post training behavioural change can be noted and assessed for further evaluation of training. The requirement of training of an individual can be assessed based on the performance, weaker areas need to be identified and improved subsequently.
Level-IV: Result/ Impact
The ultimate impact of the training programme can also be assessed in the form of several indicators. This type of evaluation should be carried out every 6-12months. Performance of the trainees field area can be assessed by various indicators such as number of cases detected before the training and 12 months or more after the training keeping in mind the targets fixed for each area, proportion of paediatric cases among new cases detected and various other indicators listed in the training module. Initially these cases may increase due to detection of more cases due to training of the individual but eventually over a period of time the number of cases detected will decrease. Service components also will be increased such as proportion of private practitioners sensitised, proportion of total general out patients referred for testing, positivity rate, number of practitioners and subordinate staff trained etc. the implementation of innovative approaches for addressing specific field level problems required to be identified and appraised accordingly.
The National level Institutions/ CTD will assess the level III and level IV performance, while level I and level II performance need to be assessed at the respective training sites. The formats for the evaluation at the institution level should be in consultation with the training team as listed above.
Annexures
AnnexuresThe list of the annexures is available here. The different items may be accessed by clicking on the individual items.
- Guide for Course-coordinators on LMS
- Cadre-wise Trainers' manual for different courses.
- Trainers' Guide for Health Volunteers Course
- Trainers' Guide for Pharmacists (SDS & DDS) Course
- Trainers' Guide for STS Course
- Trainers' Guide for STLS Course
- Trainers' Guide for LT (Microscopy & NAAT)
- Trainers Guide for CHO/MPW Course
- Trainers' Guide for Program Manager's course
- Trainers' Guide for MO-TC Course
- Trainers' Guide for MO-PHI Course
Guide for Course-coordinator on LMS
Guide for Course-coordinator on LMSThe Course coordinator's guide can be accessed here:
WIP
The role of course coordinator is of paramount importance for training the TB workforce using the modernized training system. S/he needs to coordinate with different stakeholders for smooth conduction of training.
For eg. Coordination with the trainer/facilitator for his/her availability for taking the training.
Coordination with ECHO relationship manager for the ECHO-zoom links for webinar. He needs to perform
Login to the platform:
Step 1: Open Swasth e-Gurukul | Spreading Knowledge Faster (swasth-egurukul.in)) on your browser window. (https://cms. swasth-egurukul.in)

Step 2: Enter your login credentials (Provided to you during your training). The dashboard page will open in the browser window.
Scheduling the course on Swasth-eGurukul:
1. Click on ‘Schedule a course’ and the tab will open which requires certain fields:
I. The field needs to be filled meticulously:
1. Course name: to be selected from the drop down menu. Select ‘Course Name’ for the target audience
2. Rename selected course name as ‘<Full State Name> State Health Volunteers training on NTEP <Month Year>’. For eg. Uttar Pradesh State Health Volunteers training on NTEP July 2021
3. Start Date: to be selected from the calendar. Date may be selected 2-3 days before the scheduled date of course starting. This will enable participants to complete enrolment, access and complete pre-test.
4. End date: to be selected from the calendar that pops up after clicking the field. The end date will be based on the number of days the course is expected to run.
5. Stage type: The frequency of sessions may be adjusted here. In Health Volunteers course it is recommended that the stage type is kept as Daily. On the basis of the stage type (daily/weekly/monthly) and the number of corresponding intervals between the start-date and the end-date, there will be a related number of stages available for dividing the course sessions into. Eg if the start date is 1/2/2021 and end date is 28/2/2021, corresponding to 28 days; setting stage type as daily will give 28 stages, and setting stage type as weekly will give 4 stages.
6. Certificate: The certificate for the course needs to be chosen from the list of templates available from the drop down menu.
7. State: This field helps filtering the training aspirants from a particular state. The registered trainees from the selected state will be able to join the course.
8. Moderator: From the drop-down menu, facilitator/trainer needs to be selected. One or multiple facilitator may be selected for the same course but for different sessions.
The facilitators are registered by the Project-admin and login credentials are created for them. After this, their names are included in the drop down menu.
The filled up fields appears like this (image below):
II.The next important step is setting the stages in which course needs to scheduled. Only on this particular date and chronology the course will become live on portal.
All the stages (at the level of chapters) needs to be set individually.
The dates and facilitator may be changed as per the training plan. Once the date is changed for a particular session inside a stage, all the dates for the subsequent sections changes automatically and is set to be after that date.(image below)
After clicking ‘Schedule’ the course scheduling progress tab opens. It may take while to schedule the course. Do not stop or refresh your browser window during this process.(image below)
Admitting trainees to a course:
1. On opening this tab, the course list is available. The course coordinator needs to click the course s/he has scheduled and the list of people who have enrolled for the course will be displayed.
2. The course-coordinator need to approve the trainees who have been shortlisted for this particular course (on the basis of training plan) and may disapprove the rest/non-qualified enrolees.(image below)
Scheduling webinars:
Webinars need to be scheduled inside the course for various virtual sessions that the participants need to join. The Course Coordinator needs to get in touch with the corresponding ECHO relationship manager to create the ECHO Meeting link.
1. The webinars are scheduled for the instructor to train the participants virtually using the ECHO-zoom link. The fields name is to be entered in a standardised manner.
2. Course: To be selected form the drop down menu. The course which has scheduled by the course-coordinator should be selected as the choice here.
3. Webinar title: The webinar to be titled in standardised manner as: Course name - Day 0 and so on. Eg. Uttar Pradesh State Health Volunteers training on NTEP July 2021 - Day0, Uttar Pradesh State Health Volunteers training on NTEP July 2021 - Day 1, etc.
4. Starting date and time:
a. The webinar may be scheduled on or after the start date of the course.
b. A webinar Day 0 may be planned as an ice-breaker session to establish rapport between and the trainer and the trainees and to explain the participants the structure of the training and to share other relevant details.
c. Upon scheduling the enrolled trainees will get the webinar link. The trainees also receive a reminder email from LMS on the day of webinar. The link will also be sent to the facilitators The trainees and facilitators may click the link and access the zoom meeting.
5. Duration of meeting: To be entered in minutes
6. Facilitator: It has to be selected from the drop down menu from the list of facilitators already added by project admin.
7. Use meeting licence: It has to be changed to “External” and the Echo zoom link provided by the ECHO relationship manager for the specific webinar needs to be entered here.
8. Webinar enrolment limit: By default, it has been set to 500. But, it may be changed depending on number of participants expected to join the webinar. After entering all these details, on clicking the ‘schedule’ button, the webinar is scheduled. (image below):
9. After scheduling, the tab displays the number of participants enrolled for course. The participants enrolled and approved for the course automatically becomes the recipient of webinar link. The course coordinator may see the list and status of webinar scheduled by him under the tab- ‘my webinars’(Image below)
Discussion board
It may be used by the trainees and trainer alike to post queries and respond to the comments and
queries. (Image below)
Monitoring the progress of Training
Training report: This tab gives the summary of scheduled courses. It also gives the overall summary
of the course progress, like how many trainees have enrolled for course, how many have started the
training, how many have completed the training, feedback received, etc. (Image below):
On clicking the course, the detailed training report of all the trainees opens. The course-coordinator
can see the progress of each trainee- the enrolment date, trainee’s progress on course, etc. This is
particularly helpful in reaching out to those trainees who are facing difficulty with the training.
(Image below):
Trainers' Guide for Health Volunteers Course
Trainers' Guide for Health Volunteers CourseTrainees
The targeted trainees for this course are generally those persons at the community level who would be interacting with the population for the purpose of on-ground TB activities related to awareness, screening and Treatment Support. These may include:
- ASHA Workers
- Volunteers from NGOs, Community Representatives/ Youth Volunteers
- TB Champions / Survivors/ Family Members
- Workplace Representatives who volunteer for becoming focus for TB Services
- Educators/ Teachers from Schools and Colleges
Trainers
The following cadres are supposed to be trained to become trainers on this course.
- STS
- TB HV
- MO-PHI
- MPHW/ Block Coordinators (NHM trainers)
- DPC/ PPM Co-ordinators
- NGO coordinators/ Supervisors
- Representatives from Private/ Corporate sector
The capacity of these trainers to conduct the training for health volunteers will be in-built into their training and is considered as one of their essential competencies.
Training Methods
Teaching and discussing the course content using the standardised training content available on the NTEP approved LMS (such as Swasth-eGurukul). This training may use blended training delivery methods that are appropriate to the local context. This would include a mix of the following options
- Training Premises
- In-person
- virtual
- Mode of delivery
- Facilitator led
- Self learning
- Demonstrations
- practical exercises.
In the blended mode, an instructor-led session should be conducted for each chapter. Simultaneously the trainees would go through the content available online themselves according to the schedule. Trainees need to attempt the quizzes after each chapter/module.
At the end of each chapter/session the trainer/ facilitator should summarise the key messages of the chapter by engaging trainees through questions and discussions. The discussion should focus on aspects related to the competencies listed below. These sessions should also help the trainees to clarify doubts and queries.
For the training areas which require hand-holding of trainees like to perform actual processes such as filling of forms, counselling/ addressing stigma, screening, sample collection, adherence monitoring, a demonstration/ role play mode may be adopted.
The duration of training content including discussions/ demonstrations/ role play, pre/post training assessments, is expected to be completed 6 hours. The course coordinator may schedule the course in multiple sessions totaling to this duration as appropriate.
Pre-training Preparation
Before starting a batch of training, the following preparations need to be completed.
- Creation/ confirmation/ Issue of Ni-kshay Usernames to the Health Volunteers
- Preparation of Props (Drug Blister packs, PWB, Specimen collection container, falcon tube, Specimen carry bags, IEC Materials)
Chapter wise Trainers notes
The course is divided into three modules, with a total of 12 chapters, each with specific learning and training objectives in alignment with the competencies of the person.
The different scenarios and probes for the conversation and discussion have been covered in details at relevant sections. Three standard role plays have also been incorporated at the end of each module in the training course.
| Session | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Session-1 (Introduction) |
Introduction and Overview of course NOTE: This session may be used as an ice-breaking session and to establish a rapport with the participants. It may also be emphasized here the importance of pre-test, quizzes and post-test assessment to successfully finish the course and obtain the certificate. |
5 mins |
| Pre-test assessment | Note: This is Mandatory before proceeding with course content | 10 mins |
| Module 1. Basics of TB and NTEP (120 mins) | ||
| Chapter 1: Tuberculosis |
Emphasis points during the session
|
30 mins |
| Chapter 2: NTEP |
Emphasis points during the session
|
15 mins |
| Chapter 3-TB diagnosis and Case Finding |
Emphasis points during the session
|
15 mins |
| Chapter 4: Nikshay & Treatment Supporter |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session Activity: |
20 mins |
| Role play #1: |
A short role play with the trainees to explain the process of screening and case finding, identifying the presumptive cases, and referring them to the nearest DMC for TB diagnosis. The trainer may act as the case/patient and one participant may act as an ASHA. Scenario Brief
Probes:
|
10 mins |
| Quiz #1 | The participants need to attempt the quiz based on training content covered in Module 1. Participants should complete the quiz before moving on to Module 2. This is a pre-requisite for final certificate |
10 mins |
| Module 2: Treatment Support and Monitoring of TB Patient (90 mins) | ||
| Chapter 5- TB Treatment and Care |
Emphasis points during the session
|
40 mins |
| Chapter 6- Treatment Adherence |
Emphasis points during the session
Post session activity:
|
30 mins |
| Role play #2: |
Scenario 1: Mr Ashish who is diagnosed with TB has been initiated on first-line ATT. He was hesitant to start treatment after learning about his TB disease. He lives in an over-crowded chawl with poor hygiene. Probes: Probes Key message at the end of role play : |
10 mins |
| Quiz #2 | The participants need to attempt the quiz based on training content covered in Module 2. Participants should complete the quiz before moving on to Module 3. This is a pre-requisite for final certificate |
10mins |
| Module 3: Patient Support (120 mins) | ||
| Chapter 7 - Public Health Action |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session activity
|
25 mins |
| Chapter 8: TB Arogya Sathi Application |
Emphasis points during the session
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 9- Counselling |
Post Session activity
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 10- Social inclusion and wellness activity |
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 11: Community Engagement |
Post Session activity
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 12: Linkages to Social Support Scheme |
|
10 mins |
| Role play #3: |
Scenario: A newly diagnosed TB patient initiated on treatment comes to his hometown for home based care and treatment. ASHA worker visits his home to verify his address and upon enquiring with neighbours she learnt that Ashish is being stigmatised for contracting TB and his family is being discriminated against. Now ASHA has to give correct information regarding TB to the neighbourhood. Probes: |
15 mins |
| Quiz #3: Post - Test |
All module content will be covered in this quiz. Completion of this final quiz successfully, along with the two quizzes in-between the course is mandatory for certificate generation |
10 mins |
Roles and responsibilities of Key Stakeholders
Please refer to the general roles of various stakeholders for training of Health Volunteers (click here).
Apart from these general roles, the state NHM has an important role to play in the training of Health Volunteers, especially those who are ASHAs in the state. The state NHM needs to ensure that all the ASHAs are being trained on TB and NTEP as per the standard training content. The state ASHA cell at the NHM, should ensure that the following steps are being taken:
- Support STDC/ STC in planning the training and inclusion in PIP
- Prepare and share the list of ASHA’s in the prescribed format with the respective STDC Team
- Guide and provide directives to the respective District/ Blocks to deploy ASHA’s along with concerned supervisors to ensure active participation.
Competencies of the Health Volunteer
Competencies of the Health VolunteerThe following nine competencies are important to a health volunteer -
| Sr No | Competency | Description/ activities pertaining to the said competency | Assessment of competency |
| 1 | Talk about TB |
|
1. Observe the health volunteers talking about TB during home visits |
| 2 | Screen for TB using the 4 symptom complex |
|
1. Observe a health volunteer screening for TB during home visits |
| 3 | Refer for diagnosis to the nearest TB Testing Centre. |
|
1. Observe a referral process during the home visit, including recording of the information in Ni-kshay |
| 4 | Collect the sample from a presumptive TB and transport it to the testing facility |
|
1. Check with the laboratory regarding the quality of samples collected by the health volunteer |
| 5 | Provide Treatment adherence Support for TB Treatment and TPT* |
|
1. Review Ni-kshay / Treatment cards for Adherence scores of presently linked patients 2. Interview patients to check the kind of support they received |
| 6 | Counsel people who are on TB treatment/TPT and their family* |
|
1. Interview with health volunteers to understand the current practice. |
| 7 | Detect Adverse Drug Reactions and Refer them for timely for management* |
|
1. interview the linked patients regarding how ADR was managed for them. |
| 8 | Perform post-treatment follow-up* |
|
1. Check whether previously linked Treatment completed patients have all their post treatment follow up due completed. |
| 9 | Use Ni-kshay for performing the actions related to the above |
|
Check ability to login, enrol and refer patients to health facilities, sample collection and transportation and also mark treatment adherence in Ni-kshay during patient visit. |
The five (first four and last one) are core competencies of all volunteers while the remaining four (marked with *) are core competencies only if the volunteer acts/ intends to act as a treatment supporter.
The knowledge and training related to these competencies will be provided through the Course for Health Volunteers on NTEP and assessed through the pre and post-test assessments/ quizzes.
Competency assessment needs to be done periodically (once in two years) or at the time of registration or initiation of the treatment regimen.
Trainers' Guide for LT (Microscopy & NAAT)
Trainers' Guide for LT (Microscopy & NAAT)1. Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the “Course for Lab Technicians (Microscopy & NAAT) on NTEP” guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
● Laboratory technicians (Microscopy & NAAT) working under NTEP (program staff and General health system staff)
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstrations/ practical exercises. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the Modernised Training System, each State may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their State.
For virtual sessions, the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each module. An instructor-led session will also be conducted at the end of each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts.
For the training areas which require hand-holding of trainees like demonstration of processes- Specimen collection and transportation, smear microscopy, Using different NAAT, patient workflow in Ni-kshay, maintaining Lab Supplies, etc in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
The training course content has modules and 56 chapters. Based on different modalities used for the training, the training delivery should take at least 45 hours.
For the purpose of assessment of trainees, a pre-test before the beginning of training, interim quizzes at the end of each module and a post-test at the end of training has been configured in the course content. The certificates are auto generated for the trainees in their LMS account on successful completion of post-test and their performance in interim quizzes.
The training of LTs needs to be conducted at DTC where the required lab facilities are available.
The batch size for Physical Session should not be more than 7 participants and not more than 15 participants for virtual sessions.
2. Training curriculum / Agenda
3. Trainers
For this course, following personnel may be appointed as the trainers
- DTO
- STLS
Eligibility -
Trainers are selected based on their ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner. They must possess strong knowledge about TB laboratories and related processes in NTEP. The Trainers should have completed the ‘Course for LT(Microscopy & NAAT) on NTEP’’. The Trainers should be well versed with the IT systems such as, Zoom (for video conferencing), Swasthya-eGurukul (Learning Management System) and Nik-shay. The Trainers need to go through the Chapter- wise Training Guide for this Course, provided as an Annexure
Chapter wise detailed instructions for Trainers
The aim of providing chapter-wise detailed instructions provides the Trainers with the following:
- Module-wise and Chapter-wise, modality that may be adopted (virtual/ Physical/ In-person)
- The estimated time to complete the content.
- The key messages that a trainer should emphasize upon, while delivering the training
- The activities which should be conducted at the end of each chapter / session to ensure learning effectiveness. This may include asking specific questions, demonstrating processes, discussing various forms and equipment. If any Module specific physical visits are required to be conducted, such details are also provided here.
This guiding document will also aid in bringing uniformity with respect to the content and quality of training conducted across the entire state and nation.
| (Physical Session: 2 hour) | |
| Post Session activity |
|
||
Competencies of the Lab Technician (LT)
Competencies of the Lab Technician (LT)The following competencies are important to a LT
Trainers' Guide for Pharmacists (SDS & DDS)
Trainers' Guide for Pharmacists (SDS & DDS)Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the “Course for Pharmacists and storekeepers in NTEP” guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
- State Drug Stores Pharmacists cum storekeepers
- District Drug Stores Pharmacists
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstrations/ practical exercises. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the Modernised Training System, each State Office may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their State.
For virtual sessions, the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each chapter. An instructor-led session will also be conducted for each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts of the training participants.
For the training areas which require handholding of trainees like demonstration of processes- like filling of forms, verification of supplies, stacking, etc. in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
Training curriculum / Agenda
|
Sr. |
Trainers
For this course, following personnel may be appointed as the trainers
- SDS Pharmacists
- DDS Pharmacists (select)
- DTO (select)
- MO - STDC
- MO - STC
-
WHO-consultants
Eligibility -
Trainers are selected based on their ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner. They must possess strong knowledge about Supply Chain Management and related processes in NTEP. The Trainers should have completed the ‘Course for Pharmacists’. The Trainers should be well versed with the IT systems such as, Zoom (for video conferencing), Swasthya-eGurukul (Learning Management System), Nikshay and Nikshay Aushadhi. The Trainers need to go through the Chapter- wise Training Guide for this Course.The training of pharmacists of District and TU level to be conducted at state level.
It is recommended that the trainers are appointed from all regions of the State, so that subsequent refresher training can be conducted locally by these trainers.
Chapter wise detailed instructions for Trainers
The aim of providing chapter-wise detailed instructions provides the Trainers with the following:
- Module-wise and Chapter-wise, modality that may be adopted ( virtual/ Physical/ In-person)
- The estimated time to complete the content
- The key messages that a trainer should emphasise upon, while delivering the training
- The activities which should be conducted at the end of each chapter / session to ensure learning effectiveness. This may include asking specific questions, demonstrating processes, discussing various forms and equipment. If any Module specific physical visits are required to be conducted, such details are also provided here.
This guiding document will also aid in bringing uniformity with respect to the content and quality of training conducted across the entire state and nation.
|
Module 1: Basics of TB and NTEP Virtual Session (90 min) |
|
|||||
|
Chapter 1.1 |
TB & TB Epidemiology |
Virtual Session (26 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 1.2 |
NTEP |
Virtual Session (34 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 1.3 |
Diagnostic Technologies |
Virtual Session (16 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 1.4 |
Approaches to TB Case Finding |
Virtual Session (6 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Module 2 |
TB Treatment |
Virtual Session (203 min) |
|
|||
|
Chapter 7.1 |
General concepts in TB Treatment |
Virtual Session (45 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.2 |
DS-TB Treatment and care |
Virtual Session (10 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.3 |
DR-TB Treatment and care |
Virtual Session (20 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|||||
|
Chapter 2.4 |
Shorter Oral Bedaquiline-containing MDR/RR-TB Regimen |
Virtual Session (14 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.5 |
Longer Oral M/XDR-TB Regimen |
Virtual Session (10 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.6 |
Isoniazid (H) Mono/Poly DR-TB Regimen |
Virtual Session (5 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.7 |
TB Infection treatment and care |
Virtual Session (14 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.8 |
TB-Comorbidities and special situations |
Virtual Session (26 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 2.9 |
General Concepts in Adherence Management |
Virtual Session (48 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Module 3: General concepts and Principles of SCM in NTEP Virtual Session (114 min) |
||||||
|
Chapter 3.1 |
Key Concepts and Principles in SCM |
Virtual Session (33 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 3.2 |
Drugs and consumables in NTEP |
Virtual Session (14 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 3.3 |
Stores in NTEP |
Virtual Session (14 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 3.4 |
Patient-wise Boxes |
Virtual Session (29 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 3.5 |
Information Systems in NTEP SCM |
Virtual Session (10 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 3.6 |
Roles and responsibilities in SCM |
Virtual Session (14 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Module 4: Inventory Management in NTEP Physical Session (125 min) |
||||||
|
Chapter 4.1 |
Overview of Inventory management in NTEP |
Physical Session (8 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 4.2 |
Indenting and receipt |
Physical Session (24 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 4.3 |
Issue and consumption |
Physical Session (48 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 4.4 |
Reporting of Stocks |
Physical Session (13 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 4.5 |
Expiry Management |
Physical Session (19 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 4.6 |
Stocking NTEP drugs in Private sector |
Physical Session (13 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Module 5: Procurement in NTEP Physical Session (39 min) |
||||||
|
Chapter 5.1 |
Key concepts in Procurement |
Physical Session (13 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 5.2 |
Procurement Processes |
Physical Session (8 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 5.3 |
Government e-Marketplace [GeM] |
Physical Session (18 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Module 6: Logistics and Distribution of Drugs and consumables Physical Session (89 min) |
|
|||||
|
Chapter 6.1 |
Flow of Supplies |
Physical Session (23 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 6.2 |
Packaging |
Physical Session (35 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 6.3 |
Return and Reconstitution |
Physical Session (18 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 6.4 |
Transportation |
Physical Session (13 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Module 7 |
Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation and QA |
Physical Session (76 min) |
|
|||
|
Chapter 7.1 |
Quality Assurance of Drugs |
Physical Session (33 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 7.2 |
Monitoring of sub-stores |
Physical Session (10 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 7.3 |
Store Visits and Physical Verification |
Physical Session (15 min) |
|
|||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 7.4 |
Physical Session (13 min) |
|
||||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
|
Chapter 7.5 |
Physical Session (5 min) |
|
||||
|
Emphasis Points |
|
|
||||
|
Post Session Activity |
|
|
||||
Competencies of the Pharmacists
Competencies of the PharmacistsThe following competencies are essential to a Pharmacists
Trainers' Guide for STS Course
Trainers' Guide for STS CourseIntroduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the ‘Course for STS in NTEP’ guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
- Senior Treatment Supervisor (STS)
- Tuberculosis Health visitor (TB-HV)
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstration and role plays. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the Modernized Training System, each State Office may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their State.
The training of STS to be conducted at State/Regional level preferably at the STDC. The batch size for Physical Session/Virtual Sessions should not be more than 25.
For virtual sessions, the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each module. An instructor-led session will also be conducted for each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts.
For the training areas which require hand-holding of trainees like demonstration of processes- like patient management in Ni-kshay, filling of various forms, Adherence Management tools, recording information on Public Health action, use of NI-kshay Aushadhi, etc in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
The training course content has 11 modules and 43 chapters. Based on different modalities used for the training, the training delivery should take at least 40 hours.
For the purpose of assessment of trainees, a pretest before the beginning of training, interim quizzes at the end of each module and a post-test at the end of training has been configured in the course content. The certificates are auto-generated for the trainees in their LMS account on successful completion of post-test and their performance in interim quizzes.
Training curriculum / Agenda
|
Sr. |
Module |
Chapters |
Training Modality |
Duration (Hrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basics of TB and NTEP |
|
Virtual
|
4 |
|
2
|
TB Diagnosis and Case finding |
|
Virtual |
4
|
| 3 | TB Treatment and care |
|
Virtual |
4
|
| 4 | Adherence Management |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 5 | Public Health Action |
|
Physical |
4
|
| 6 | DBT |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 7 | Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation |
|
Physical | 4 |
| Supply Chain Management in NTEP |
|
Physical |
4
|
|
| 9 | Private sector Engagement |
|
Virtual |
2
|
| 10 | ACSM and Community Engagement |
|
3 | |
| 11 | Training the Health Volunteers and Treatment Supporters |
3
|
Trainers
For this course, following personnel may be appointed as the trainers:
- MO - STDC
- MO - STC
- WHO-consultants
- DTO (select)
- SDS/DDS Pharmacists (Select)- for Supply chain and drug distribution module.
Trainer Eligibility
Trainers are selected based on their ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner. The Trainers should have completed the ‘Course for STS’ and they must possess strong knowledge about the NTEP and the various processes related to patient workflow, Niskahy and Niskahy Aushadhi. The Trainers need to go through the Chapter- wise Training Guide for this Course, provided as an Annexure.
The Trainers should be well versed with the IT systems, for video conferencing (such as Zoom), Learning Management System (such as Swasth-eGurukul), Ni-kshay and Ni-kshay Aushadhi.
-
Chapter wise detailed instructions for Trainers
The aim of providing chapter-wise detailed instructions provides the Trainers with the following:
- Module-wise and Chapter-wise, modality that may be adopted (virtual/ Physical/ In-person)
- The estimated time to complete the content.
- The key messages that a trainer should emphasize upon, while delivering the training
- The activities which should be conducted at the end of each chapter / session to ensure learning effectiveness. This may include asking specific questions, demonstrating processes, discussing various forms and equipment. If any Module specific physical visits are required to be conducted, such details are also provided here.
This guiding document will also aid in bringing uniformity with respect to the content and quality of training conducted across the entire state and nation.
| Module 1: Basics of TB and NTEP Virtual Session (4 hours) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chapter 1.1 | TB & TB Epidemiology | Virtual Session (60 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 1.2 | NTEP | Virtual Session (45 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 1.3 | Integration of NTEP with Health System | Virtual Session(30 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Module 2 | TB Diagnosis and Case Finding | Virtual Session (4 hours) |
| Chapter 2.1 | Diagnostic Technologies | Virtual Session (30 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 2.2 | Diagnostic Network & Hierarchy | Virtual Session (30 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 2.3 | Approaches to TB Case Finding | Virtual Session (30 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
(i) Screening for active TB in a Diabetic Clinic & testing those who screened positive (ii) Screening for active TB in an elderly home & testing those who screened positive (iii) Screening for active TB in cancer wards & testing those who screened positive |
|
| Chapter 2.4 | TB Case Finding in NTEP | Virtual Session (30 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
Diagnostic algorithm for Pulmonary TB- Role of Chest X ray as a screening tool and the need to complete the diagnostic algorithm. Classification of TB on the basis of site,diagnosis, drug resistance
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Discuss: “What proportion of presumptive TB patients in your TU completes the diagnostic algorithm? What are the implications if the people are not completing the diagnostic algorithm?”
|
|
| Chapter 2.5 | Active Case Finding Campaign | Virtual Session(45 mins) |
| Emphasis Points | Step by step process in planning and execution of an ACF campaign with special emphasis on identification of target population, need for micro planning and need to prevent the leaks in the cascade of care. | |
| Post Session Activity | Discuss how they monitor the ACF in their TU against ‘Cascade of Care? What are the measures they undertake to prevent the leaks in ‘’Cascade of care’’? | |
| Module 3: | TB Treatment and care | Virtual Session (4 hours) |
| Chapter 3.1 | General Concepts in TB Treatment | Virtual Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 3.2 | DS-TB Treatment and Care | Virtual Session ( 30 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 3.3 | DR-TB Treatment and care | Virtual Session (30 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 3.4 | Different DR-TB Regimens | Virtual Session (15 mins) |
| Emphasis points |
|
|
| Chapter 3.4 | TB Infection treatment and care | Virtual Session (30 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Role Play- Counseling for TPT | |
| Chapter 3.5 | TB Co-morbidity and special situations | Virtual Session (30 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Module 4: | Adherence Management | Physical Session (4 hours) |
| Chapter 4.1 |
Patient Management |
Virtual Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
How the information of patients is managed through Ni-kshay (Enrollment, Request for Test). |
|
| Post Activity Session |
Call two participants to demonstrate how they (1) enroll a subject and (2) request for Test in Ni-kshay Make all participants to view their task list in Ni-kshay and discuss how they are going to use the feature |
|
| Chapter 4.2 | General concepts in Adherence management | Physical Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 4.3 |
|
Physical Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 4.4 | Chapter: 99 DOTS | Physical Session (30 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Scenario 1: One of their patients complained that she used to dial the toll-free number every day and used to hear “Thank You” also. But when you check, the Nikshay dashboard is still showing red.
Scenario 2: One of your clients with TB called you and told you that his call is not going to the ‘toll free’ number because of ‘insufficient’ balance. |
|
| Chapter 4.5 | Chapter: MERM | Physical Session (30 mins) |
|
||
|
||
| Chapter 4.6 | Chapter: Monitoring of adherence | Physical Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points | Participants need to be empowered to use adherence summary dashboards and interpret the indicators. | |
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Module 5: | Public Health Action | Physical Session (4 hours) |
| Chapter 5.1 | Patient Support | Physical Session (60 min) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 5.3 | Contact Investigation | Physical Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 5.4 | Counselling and Education | Physical Session (60 mins) |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Module 6: | DBT | Physical Session (4 hours) |
| Chapter 6.1 | General Concepts in DBT | 60 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
This is an overview chapter.
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 6.2 | Processes in DBT | 150 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Module 7 | Supervision, Monitoring & Evaluation | Physical (4 hours) |
| Chapter 7.1 | Supervision | 60 minutes |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 7.2 | Program Monitoring Indicators | 120 minutes |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Assignment: Each participant needs to calculate any 3 indicators in their TU based on real time data and interpret those indicators.
|
|
| Module 8 | Supply Chain Management | Physical (4 hours) |
| Chapter 8.1 | General Concepts | 60 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
General Concepts of SCM
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Ask for any doubts from the participants and clarify the same. | |
| Chapter 8.2 | Stocking Norms | 30 mins |
| Emphasis Points | Buffer stocks and storage norms | |
| Post Session Activity | Reinforce the concepts of buffer stock and storage norms. | |
| Chapter 8.3 | Supply chain process | 150 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 8.4 | Drug dispensation Module | 30 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Module 9 | Multisectoral Sector Engagement | Virtual (2 hours) |
| Chapter 9.1 | General Concepts | 30 mins |
| Emphasis Points | Why private sector engagement is important and what is the Vision of NTEP on private sector engagement. | |
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 9.2 | Models of Private Sector Engagement | 60 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain PPSAs, Direct Option for engagement. Explain STEPS |
|
| Post Session Activity | Ask each of the participants to think what model suits for private sector engagement in their TU and why. | |
| Chapter 9.3 | Partnership Guidelines | 30 mins |
| Emphasis Points | Emphasis on various options under partnership options | |
| Post Session Activity | Discuss what all partnership options are currently existing in their TUs and what would they want to have. | |
| Chapter 9.4 | Regulations | 30 mins |
| Emphasis Points | Regulations of Mandatory TB Notification and Schedule H1 | |
| Post Session Activity | Discuss how information from schedule H1 could be used? (Clue: Most crucial field in the schedule H1 register is the name of the provider who prescribed it. Information from Schedule H1 register could be used to Identify the provider prescribing the anti TB drugs and prioritize for engagement, Identify missing TB cases) | |
| Module 10 | ACSM and Community Engagement | Physical (3 hours) |
| Chapter 10.1 | General Concepts in ACSM | 60 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | ||
| Chapter 10.3 | Protocols for ACSM activities | 60 mins |
| Emphasis Points | Organising Community Meetings, Peer group interventions, ACSM activities in schools | |
| Post Session Activity | Discuss experiences form 1-2 participants regarding organizing community meetings | |
| Chapter 10.4 | Community Engagement | 60 mins |
| Emphasis Points |
LSGs and their role in TB Elimination TB Forums and what they can do What role can TB Champions play? |
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss what needs to be done to reduce stigma regarding TB in the community. Encourage everybody to discuss. | |
Competencies of the Senior Treatment Supervisor (STS)
Competencies of the Senior Treatment Supervisor (STS)The following competencies are essential to a STS
Trainers' Guide for STLS Course
Trainers' Guide for STLS Course1. Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the “Course for STLS in NTEP” guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
● Senior TB Laboratory Supervisors
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstrations/ practical exercises. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the Modernised Training System, each State may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their State.
For virtual sessions, the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each module. An instructor-led session will also be conducted at the end of each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts.
For the training areas which require handholding of trainees like demonstration of processes- Specimen collection and transportation, smear microscopy, using different NAAT, patient workflow in Ni-kshay, maintaining Lab Supplies, etc in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
The training course content has 15 modules and 56 chapters. Based on different modalities used for the training, the training delivery should take 60 hours (including demonstrations)
For the purpose of assessment of trainees, a pre-test before the beginning of training, interim quizzes at the end of each module and a post-test at the end of training has been configured in the course content. The certificates are auto generated for the trainees in their LMS account on successful completion of post-test and their performance in interim quizzes.
The training of STLS needs to be conducted at STDC/IRL where all the lab facilities are available.
The batch size for Physical Session should not be more than 7 participants and not more than 25 participants for virtual sessions.
2. Training curriculum / Agenda
3. Trainers
For this course, following personnel may be appointed as the trainers
- STDC- Medical Officers
- IRL Microbiologist
- EQA Microbiologist
- NRL Microbiologist
- WHO consultants
Eligibility -
Trainers are selected based on their ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner. They must possess strong knowledge about TB laboratories and related processes in NTEP. The Trainers should have completed the ‘Course for STLS on NTEP’’. The Trainers should be well versed with the IT systems such as, Zoom (for video conferencing), Swasthya-eGurukul (Learning Management System) and Nik-shay. The Trainers need to go through the Chapter- wise Training Guide for this Course, provided as an Annexure
Chapter wise detailed instructions for Trainers
The aim of providing chapter-wise detailed instructions provides the Trainers with the following:
- Module-wise and Chapter-wise, modality that may be adopted (virtual/ Physical/ In-person)
- The estimated time to complete the content.
- The key messages that a trainer should emphasize upon, while delivering the training
- The activities which should be conducted at the end of each chapter / session to ensure learning effectiveness. This may include asking specific questions, demonstrating processes, discussing various forms and equipment. If any Module specific physical visits are required to be conducted, such details are also provided here.
This guiding document will also aid in bringing uniformity with respect to the content and quality of training conducted across the entire state and nation.
| (Physical Session: 2 hour) | |
| Physical Session (8 hours ) | |
| (Physical Session: 08 hours) | |||
| Practical Exercise on CBNAAT | Physical (180 mins) | ||
| (Physical Session: 08 hours) | |||
| Practical Exercises on Truenat | Duration: 3 hours | ||
| Physical (60 mins) | |||
| Post Session activity |
|
||
| Physical Session (3 hours) | |
| Virtual Session (2 hours) | |
| Virtual Session (6 hours) | |
| Virtual (1 hour) | |
| Virtual (2 hours) | |
| Virtual (120 mins) |
| Virtual Session ( 2 hours) |
| Virtual (60 mins) |
| Virtual Session (2 hour) |
| Virtual (60 mins) |
| Virtual Session (30 mins) |
| Virtual (30 mins) |
Competencies of the STLS
Competencies of the STLSThe following competencies are essential to an STLS.
Trainers' Guide for CHO/MPW Course on NTEP
Trainers' Guide for CHO/MPW Course on NTEPIntroduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the “Course for CHO/MPW-PHI on NTEP” guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
- Community Health Officers (Stationed at AB-HWCs)
- Multi-purpose workers (stationed at PHI)
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstrations/ practical exercises. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the NTEP Training System, each State may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their State.
For virtual sessions, the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each module. An instructor-led session may also be conducted at the end of each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts.
For the training areas which require handholding of trainees like demonstration of processes- Counselling about Specimen collection, patient workflow in Ni-kshay, etc. in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
The training course content has 3 modules and 16 chapters. Based on different modalities used for the training, the training delivery should take at least 8 hours.
For the purpose of assessment of trainees, a pre-test before the beginning of training, interim quizzes at the end of each module and a post-test at the end of training has been configured in the course content. The certificates are auto generated for the trainees in their LMS account on successful completion of post-test and their performance in interim quizzes.
The training of CHOs/MPWs needs to be conducted at DTC/Block level wherever adequate facilities are available.
The batch size for in-person Session should not be more than 15 participants and not more than 30 participants for virtual sessions.
Pre-training Preparation
Before starting a batch of training, the following preparations need to be completed.
- Creation of Nikshay Usernames to the Community Health Officers
- Preparation of Props (Drug Blister packs, PWB, Specimen collection container, falcon tube, Specimen carry bags, IEC Materials, etc.)
Chapter wise Trainers notes
The course is divided into three modules, with a total of 16 chapters, each with specific learning and training objectives in alignment with the competencies of the person.
The different scenarios and probes for the conversation and discussion have been covered in details at relevant sections. Three standard role plays have also been incorporated at the end of each module in the training course.
| Session | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Session-1 (Introduction) |
Introduction and Overview of course NOTE: This session may be used as an ice-breaking session and to establish a rapport with the participants. It may also be emphasized here the importance of pre-test, quizzes and post-test assessment to successfully finish the course and obtain the certificate. |
5 mins |
| Pre-test assessment | Note: This is Mandatory before proceeding with course content | 10 mins |
| Module 1. Basics of TB and NTEP (180 mins) | ||
| Chapter 1: Tuberculosis |
Emphasis points during the session
|
30 mins |
| Chapter 2: NTEP |
Emphasis points during the session
|
15 mins |
| Chapter 3-TB diagnosis and Case Finding |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session Activity:
|
15 mins |
| Chapter 4: Nikshay & Treatment Supporter |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session Activity: |
20 mins |
| Chapter 5: TB Arogya Sathi Application |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session Activity:
|
30 mins |
| Chapter 6: Patient Management in Ni-kshay |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session Activity: Username: tbu-kadha01 Password: Test@123 |
60 mins |
| Role play #1: |
A short role play with the trainees to explain the process of screening and case finding, identifying the presumptive cases, and referring them to the nearest DMC for TB diagnosis. The trainer may act as the case/patient and one participant may act as an ASHA. Scenario Brief
Probes:
|
10 mins |
| Quiz #1 | The participants need to attempt the quiz based on training content covered in Module 1. Participants should complete the quiz before moving on to Module 2. This is a pre-requisite for final certificate |
10 mins |
| Module 2: TB Treatment and Monitoring (150 mins) | ||
| Chapter 7- General Concepts in TB treatment |
Emphasis points during the session
Post session activity:
|
30 mins |
|
Chapter 8: DS-TB Treatment and care
|
Emphasis points during the session
Post session activity:
|
30 mins |
| Chapter 9: DR-TB treatment and care |
Emphasis points during the session
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 10: Treatment Adherence |
Emphasis points during the session
Post session activity:
|
30 mins |
| Role play #2: |
Scenario 1: Mr Ashish who is diagnosed with TB has been initiated on first-line ATT. He was hesitant to start treatment after learning about his TB disease. He lives in an over-crowded chawl with poor hygiene. Probes: Probes Key message at the end of role play : |
30 mins |
| Quiz #2 | The participants need to attempt the quiz based on training content covered in Module 2. Participants should complete the quiz before moving on to Module 3. This is a pre-requisite for final certificate |
10mins |
| Module 3: Patient Support (150 mins) | ||
| Chapter 11 - Public Health Action |
Emphasis points during the session
Post Session activity
|
30 mins |
| Chapter 12- Counselling |
Post Session activity.
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 14- Social inclusion and wellness activity |
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 15: Community Engagement |
Post Session activity
|
20 mins |
| Chapter 16: Linkages to Social Support Scheme |
|
20 mins |
| Role play #3: |
Scenario: A newly diagnosed TB patient initiated on treatment comes to his hometown for home based care and treatment. ASHA worker visits his home to verify his address and upon enquiring with neighbours she learnt that Ashish is being stigmatised for contracting TB and his family is being discriminated against. Now ASHA has to give correct information regarding TB to the neighbourhood. Probes: |
30 mins |
| Quiz #3: Post - Test |
All module content will be covered in this quiz. Completion of this final quiz successfully, along with the two quizzes in-between the course is mandatory for certificate generation |
10 mins |
Trainers' Guide for Program Manager's course
Trainers' Guide for Program Manager's courseIntroduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the ‘Course for Program Managers in NTEP’ guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
- District Program Managers- District TB Officer (DTO)
-
State Program Managers- State TB Officer (STO)
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstration and role plays. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the Modernized Training System, the training institute may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their trainees.
The training of DTOs is to be conducted at National Institutes (NITRD/NTI) or at select STDCs across country as decided by Central TB Division. The training of STOs is however be conducted at the national Institutes only.
The batch size for Physical Session/Virtual Sessions should not be more than 25.
Virtual sessions: the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each module. An instructor-led session will also be conducted for each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts.
Physical/In-person Sessions: For the training areas which require hand-holding of trainees like demonstration of processes- like patient management in Ni-kshay, filling of various forms, Adherence Management tools, recording information on Public Health action, use of NI-kshay Aushadhi, etc in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
The training course content has 14 modules and 61 chapters. Based on different modalities used for the training, the training delivery should take at least 80 hours.
For the purpose of assessment of trainees, a pre-test before the beginning of training, interim quizzes at the end of each module and a post-test at the end of training has been configured in the course content.
Some exercises have also been formulated to assess and reinforce the learnings of the trainees based on their job requirements. These exercise will be communicated to the trainees either before the beginning of in-person sessions and the solutions of which will be discussed during the physical sessions.
The other exercises will be given to trainees during the conduct of the training and will be discussed simultaneously.The certificates are auto-generated for the trainees in their LMS account on successful completion of post-test and their performance in interim quizzes.
Training curriculum / Agenda
| Sr. | Module | Chapters | Training Modality |
Duration (Hrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basics of TB and NTEP |
|
Self-Reading/Virtual
|
6 |
|
2
|
TB Laboratories and Diagnostic technologies in NTEP |
|
Self-Reading/Virtual | 6 (including Lab/Field visit) |
| 3 | TB Diagnosis and Case finding |
|
Physical |
6
|
| 4 | TB Treatment |
|
Physical | 10(including field visit) |
| 5 | TB and comorbidity management |
|
Physical | 3 |
| 6 | Public Health Action |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 7 | TB Prevention |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 8 | Direct Benefit Transfer in NTEP |
|
Physical |
6
|
| 9 | Financial management and Planning |
|
Physical | 3 |
| 10 | Procurement, Supply Chain Management & Preventive Maintenance |
|
Physical | 6 |
| 11 | Partnerships, Corporate and Multisectoral engagement |
|
Physical | 4 |
|
12
|
ACSM and Community Engagement |
|
Physical | 4 |
|
13
|
Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 14 | Training and capacity development | Physical | 3 |
Trainers:
For this course, personnel that have been trained and certified by Central TB Division for conducting this course at national level may only act as trainers. These may include personnel from Central TB Division, National Institutes, Technical Partner Organizations, STDCs and Medical Colleges. Central TB Division will maintain the latest list of certified trainers and need to be referred to before conducting the training.
Trainers are selected based on the following aspects
- Ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner.
- Strong knowledge about the NTEP and the various processes related to patient workflow, Ni-ksahay and Ni-kshay Aushadhi; demonstrated by completing the entire question bank related to the modules they are certified to train.
- Proficient in this Chapter- wise Training Guide.
- Well versed with the IT systems such as, Zoom (for video conferencing), Swasth-eGurukul (Learning Management System), Ni-kshay and Ni-kshay Aushadhi.
Chapter wise instructions for Trainers
The aim of providing chapter-wise detailed instructions provides the Trainers with the following:
- Module-wise and Chapter-wise, modality that may be adopted (Self-reading/virtual/ Physical/ In-person)
- The estimated time to complete the content.
- The key messages that a trainer should emphasize upon, while delivering the training
The activities which should be conducted at the end of each chapter / session to ensure learning effectiveness. This may include asking specific questions, demonstrating processes, discussing various forms and equipment. If any Module specific physical visits are required to be conducted, such details are also provided here.
Some exercises have also been provided with the relevant chapters that the trainees need to finish as the part of curriculum. The trainers should ensure that all the trainees finish these exercises individually and record it in appropriate response forms. All the exercise should be discussed by the trainers during the training.
This guiding document will also aid in bringing uniformity with respect to the content and quality of training conducted across the entire state and nation.
| Module 1: Basics of TB and NTEP | |
|---|---|
| Chapter 1.1 | TB & TB Epidemiology |
| Emphasis Points | 1. Difference between Incidence and notification 2. Difference between Exposure to TB, infection and TB disease. |
| Post Session Activity |
These exercises are to be given as assignments that trainees need to finish before start of 2nd module. Assignments:
|
| Chapter 1.2 | NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post Session Activity |
Discuss- ‘What India is committed to achieve in 2025 in relation to ending TB?’’ [Clarify that the country is only trying to achieve the SDG goals related to Ending TB] Discuss- ‘Can Medical College/ IRL be a PHI?’[Clarify that any patient service delivery point will be a PHI, but program management units like STC, DTC, TU etc are not PHIs] Assignments:
|
| Chapter 1.3 | Approaches to S&M in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the importance of S&M. Emphasize that S&M of the different activities under NTEP will be discussed alongside the activity while discussing the content in the modules. |
| Post-session activity |
Assignment: 1.3.1- Find the index score of your district using Nikshay for year 2022. |
| Chapter 1.4 | Integration of NTEP with Health System |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the need for integration of NTEP with the general health system & NHM and how that integration is envisioned. |
| Post-session activity |
Discuss - "What are the opportunities available to NTEP through Health & Wellness Centers? How could that be materialized? Assignments: 1.4.1-Write the organisation str of NTEP in your district. |
| Chapter 1.5 | Information Systems in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post-session Activity | 1.5.1- Enlist the different stakeholders that are working with Nikshay and their specific roles in NI-kshay. |
| Module 2 | TB Laboratories and Diagnostic technologies in NTEP |
| Chapter 2.1 | Diagnostic Technologies and Lab Network |
| Emphasis Points | Names of different tests, their uses, advantages and disadvantages |
| Post-session Activity |
Discuss: what are the advantages and disadvantages of FL- LPA over NAAT? Discuss “how many sputum collection and transportation facilities are there in their concerned district? Make one participant explain how it functions and what are the benefits out of it”? - Bring out the following benefits (1) prevents leaks in cascade of care (reduce loss from presumptive TB identification to TB Testing) (2) minimizes patient inconveniences (3) minimize patient Turnaround Time (4) reduce out of pocket expenditure (5) helps in infection control as people with symptoms need not travel Assignment: 3.1.1Learn about the processes being followed in your district for sample transport from patient to TDC. |
| Chapter 2.2 | TB detection Centres |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the consumables required for the Microscopy, CBNAAT and Truenat |
| Post-session Activity |
Assignments: A Lab-visit needs to be organised for participants to see the different processes involved for testing. |
| Chapter 2.3 | Specimen collection and transportation |
| Emphasis Points |
The need for SCT, importance of cool chain requirement. Discuss how the delays can be reduced to improve the TAT overall |
| Post Session Activity | May ask one of the participants to volunteer and demonstrate the different processes being followed in Nikshay for the same- i.e. adding test request, sample details and result updation in Ni-kshay. |
| Chapter 2.4 | Quality Assurance of TDC |
| Emphasis Points | Explain the process involved in EQA of microscopy. |
| Post-session Activity |
Lab Field visit: A field visit should be organized to a lab to understand and discuss the following:
3) Obtain the Lab register from Nikshay and calculate the patient TurnAroundTime (referral to test reporting) for the lab and compare it with the Lab TurnAroundTime (Sample Receipt to Reporting) |
| Module 3 |
TB Diagnosis and Case finding |
| Chapter 3.1 | General Concepts in TB Case Finding |
| Emphasis Points | Differentiate between screening and testing. |
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter 3.2 | Approaches to TB Case Finding |
| Emphasis Points | Clearly differentiate the difference between the three different approaches- Active, Passive and Intensified. |
| Post-session Activity |
(i) Screening for active TB in a Diabetic Clinic & testing those who screened positive (ii) Screening for active TB in an elderly home & testing those who screened positive (iii) Screening for active TB in cancer wards & testing those who screened positive |
| Chapter 3.3 | Diagnostic Algorithms in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss how the algorithms to be read |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to look at details of 5 TB patients from their district and see whether complete diagnostic algo has been followed or not. |
| Chapter 3.4 | Active Case Finding Campaign |
| Emphasis Points | Step by step process in planning and execution of an ACF campaign with special emphasis on identification of target population, need for micro planning and need to prevent the leaks in the cascade of care. |
| Post-session Activity | Discuss how ACF campaign is carried in participants district and how the activity can be carried out more effectively. |
| Chapter 3.5 | S&M for Case finding activities in NTEP. |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the TB index dashboard. Discuss the TB Notification dashboard, |
| Post-session Activity | The participants may be asked to access the TB index dashboard and TB notification dashboard from their logins and share their learnings with other audience. |
| Module 4 | TB Treatment |
| Chapter 4.1 | General Concepts in TB Treatment |
| Emphasis Points |
It's an overview chapter explaining the concepts- Fixed Dose Combination, Intensive & Continuation Phase.
|
| Post-session Activity | Request two participants to demonstrate in Demo Ni-kshay the ‘Transfer’ of patients using (i) Push and (ii) Pull methods. |
| Chapter 4.2 | ADRs to ATT |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss about the aDSM available in Ni-kshay , the importance and how it is carried out. |
| Post-session Activity | Ask one of the participants to demonstrate the adverse event module in Ni-kshay from reporting, management and outcome. |
| Chapter 4.3 | DS-TB Treatment and Care |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 4.4 | Overview of DR-TB |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain:
|
| Post-session Activity | Ask participants for doubts and help them clear those doubts. |
| Chapter 4.5 | Isoniazid [H] Mono/Poly DR-TB Regimen |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the regimen composition and duration, inclusion-exclusion criterion, replacement sequence and the follow-up examination. |
| Post-session Activity | May ask the participant to look at 2 TB patients (outcome declared) on H Mono/poly DR-TB regimen whether the follow-up sputum examination was done timely or not. |
| Chapter | Shorter Oral Bedaquiline-containing MDR/RR-TB Regimen |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the regimen composition and duration, inclusion-exclusion criterion, replacement sequence and the follow-up examination. |
| Post-session activity | May ask participants to look at 2 TB patients (outcome declared) on shorter oral Bdq containing MDR/RR regimen whether all the relevant investigations for PTE and follow-up sputum examination were carried out timely. |
| Chapter | Longer Oral M/XDR-TB Regimen |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the regimen composition and duration, inclusion-exclusion criterion, replacement sequence and the follow-up examination. |
| Post-session activity | May ask participants to look at 1 TB patient (outcome declared) on longer oral M/XDR regimen whether all the relevant investigations for PTE and follow-up sputum examination were carried out timely. |
| Chapter 4.6 | Treatment Support |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the role of treatment supporter and how they can be registered in Nikshay, patient mapped. |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to practice the registration of treatment supporter and subsequent mapping of patients to the treatment supporters in demo-version in Ni-kshay. |
| Chapter 4.7 | Adherence Management |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter | Monitoring of Treatment |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the indicators used in monitoring the treatment- treatment initiation, outcome declaration. |
| Post-session activity |
Exercise: Ask the participants to download the notification register for Q1-2023 and ask them to calculate the average delay in treatment initiation from date of diagnosis. Discuss how this delay can be minimised. |
| Field Activity |
A 2nd field visit(Batch size- 5-7 participants) should be organised to the following
|
| Module 5 |
TB and comorbidity management |
| Chapter 5.1 | TB and HIV |
| Emphasis Points | Bidirectional screening for TB-HIV |
| Post-session activity | Ask the participants to describe the existing mechanism at their district to screen TB among the people visiting ICTC centres- how is the screening being done? How is it ensured that all those referred for testing have undergone testing? Discuss if there is any scope for improvement. |
| Chapter 5.2 | TB and Diabetes |
| Emphasis Points | Bidirectional screening for TB-Diabetes |
| Post-session activity | Ask the participant to describe how diabetes testing is done among people with TB in their district? What are the steps if a person with TB is found to have diabetes? Who and how is diabetic control ensured for that person? Discuss if there are any ways to improve. |
| Chapter | TB and malnourishment |
| Emphasis Point: | Discuss how malnourishment affects TB patient and role of Nutritional support in successful completion of treatment. |
| Chapter | TB and Substance Abuse |
| Emphasis Point: | Discuss how Alcohol and Tobacco Abuse affects TB and importance of linkage with the deaddiction centre. |
| Post Session Activity | The participants may be asked to list the de-addiction centres and tobacco-caseation centres. |
| Chapter | TB and other comorbid conditions |
| Module 6 | Public Health Action |
| Chapter 6.1 | Patient Support |
| Emphasis Points | Various kinds of support the TB patient needs (nutritional support, psychosocial support, support for deaddiction, travel support) and how STS could help in offering the same |
| Post-session activity | Give a scenario: A 62 year old woman from a Tribal community affected with TB. Ask all participants to list out all the Government schemes/initiatives which can support her during the treatment period? Write down all schemes in a flip chart/Chatbox/Virtual board |
| Chapter 6.2 | Contact tracing and investigation. |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 6.3 | Counselling |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 6.4 | TB Arogya Sathi App |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the various information available in TB Arogya Sathi Application-
|
| Post-session Activity | The participants may be requested to do a screening test on themselves and check the working of the application. |
| Module 7 | TB Prevention |
| Chapter 7.1 | Infection Prevention and Control |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 7.2 | TB Preventive Treatment |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to download the Contact tracing register (for Q3-2022) and comment on the leakages in the cascade of care for TPT for your district. |
| Chapter 8.1 | General Concepts in DBT |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter 8.2 | Processes in DBT |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter 8.3 | Monitoring of DBT |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Module | Financial management and Planning |
| Chapter 9.1 | Overview of PIP |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | May ask the participants for any doubts/queries. |
| Chapter 9.2 | Needs assessment for Planning |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | May ask the participants to clear their doubts |
| Chapter 9.3 | Preparing a PIP and Implementing the plan |
| Emphasis Points | |
| Post-session activity | May give one PIP format to the participants and ask them to fill it for their district. |
| Chapter 9.4 | Financial expenditure and accounting |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain the following.
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Module | Procurement, Supply Chain Management & Preventive Maintenance |
| Chapter | General Concepts in SCM |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain the following concepts:
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter | Information system for SCM in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following: Ni-kshay Aushadhi Different dashboards- State/district/Alert/Reports and features available at different levels. |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to open their district dashboard and look at the alert dashboard and share the finding with other participants. |
| Chapter | Processes in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss and demonstrate the participants the following processes:
|
| Post-session Activity |
Ask the participant to demonstrate the following in demo version of Ni-kshay AUshadhi:
Ask the participants to demonstrate the following in demo version of Nikshay
Ask the participants to forecast the supplies (for DS-TB drugs) for next quarter on the basis of consumptions based in previous quarter in their district
|
| Chapter | Procurement in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain the following points: Procurement- meaning and importance. Different types of procurement processes- Direct and tendering Government e-Marketplace - meaning and different processes involved. |
| Post-session Activity | The trainer may demonstrate them the processes involved in GeM using the demo version/live version using their login credentials. |
| Chapter | Quality Assurance in Supply Chain Management |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points: Meaning and Processes involved in QA of drugs in NTEP Recording of QA of drugs in Ni-kshay AUshadhi Monitoring of drug stores Store visits in NTEP- checklist for store visits Physical verification of supplies and recording in Ni-kshay Aushadhi |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participant to open demo Ni-kshay aushadhi and demonstrate the recording of Physical Stock verification, and QA of drugs |
| Module | Partnerships, Corporate and Multisectoral engagement |
| Chapter 10.1 | General Concepts in Partnership and MSE |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session activity | |
| Chapter 10.2 | Models of Partnerships |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following-
|
| Post session activity. | May ask the participants to clear their doubts. |
| Chapter 10.3 | Establishing the partnerships |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following: Guidance Document on Partnership- Overview Undertaking a needs assessment Mapping of the stakeholders- meaning and process Partnership Options- meaning and significance. Steps to engage a service delivery. Partnership options available to Private sector engagement Bundling approach- meaning and significance Contract- Meaning, Types: input-based, Output-based, Fee for service contract, Steps for executing a contract. Budgeting for Partnership options Performance matrix for partnerships Verification and validation of invoices |
| Post Session activity | The participants may clear their doubts. |
| Multisectoral Engagement | |
Competencies of the Program Managers (PM) at district level
Competencies of the Program Managers (PM) at district levelThe following competencies are important to a PM
| Competency | Description/ activities pertaining to the said competency | Assessment of competency |
|---|---|---|
| Implement the NTEP in the district as per guidelines |
|
|
| Prepare Program Implementation Plan for NTEP |
|
1. Verify PIP. 2. Interview with the DTO to identify the current practices regarding planning |
| Monitor NTEP performance |
|
1. Verify action-oriented feedback provided by the program manager 2. Verify Minutes of review meeting to check the quality of review 3. Interview with the program manager to identify the current practices regarding monitoring |
| Perform Supportive Supervision |
|
1. Verify Supervisory reports to check the quality of supervisory visits 2. Interview with the program manager to understand the current practices |
| Mange supply chain and logistics |
|
1. Interview with the DTOs to understand current practices 2. Verify records (Ni-kshay Aushadhi/Stock registers), Physical Stocks and contract records to check whether supply chain and logistics management are as per norms |
| Solve problems and improve the quality of program |
|
1. Check documents and evaluate the field realities for number of problems systematically solved by the DTO |
| Manage the training and capacity building at the district. |
|
1. Review training plan and training reports 2. Interview with staff to assess the quality of training conducted by the district 3. Review the competency assessment performed by the DTO. |
| Manage NTEP funds of the district |
|
1. Review SOEs, account book, PFMS and check whether the program manager is able to perform this function as expected 2. Interview with the program manager to understand the current practices |
| Advocate for securing resources and commitment for TB Elimination activities | 1. Check for any results of advocacy in terms of commitment from District Administration, District Health Administration, engagement of community 2. Check for the relevant meeting records |
|
| Engage Public (General Health System) and Private Healthcare Sector for TB Care |
|
1. Interview with private providers, Drug Inspector, Association leaders to check program manager's ability to engage them 2. Interview with the DTO for understanding the current practices |
| Engage Community for Ending TB |
|
1. Interview with PRI leaders, civil society leaders, TB Vijeta and the staff. 2. Review of documents of community engagement activities 3. Review the proportion of patients who are on receiving community support |
Trainer's guide for the Course for MO-PHI on NTEP
Trainer's guide for the Course for MO-PHI on NTEPIntroduction
Targeted Trainees: Medical Officer- PHI includes generally all Medical Officers placed at Government Health facilities at primary, secondary and tertiary levels. This does not include Medical Officers that have specified roles in the NTEP program, such as Medical Officers at, District / Nodal DRTB-Centres, Medical Colleges, MO-TC.
Qualified Trainers: Trainers may be other Medical Officers at the District Level or above that are prior identified by State such as DTOs, MO-TCs who are in-turn trained on their cadre's corresponding course on NTEP.
Trainers are selected based on their ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner. The Trainers should have completed their own cadre-wise course, thorough with this trainers guide and must possess strong knowledge about the NTEP, and the various processes related to patient workflow and Ni-kshay. The Trainers should be well versed with the supporting IT systems such as those for video conferencing (Zoom/ Teams/ Google meet), Learning Management System (Swasth-eGurukul), Ni-kshay, etc.
Mode of Training: Training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes may be used to execute the training.
Training Institution: The training of MO-PHI is to be organized by the District TB Centre.
Recommended Batch size: 25.
Training Duration: The training course content has 4 modules with a total of 18 chapters. A trainee needs to complete this course in about a total 16 hours. The Module wise breakup is provided below
|
Sr. |
Module |
Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basics of TB and NTEP | 2hrs |
| 2 | Case Finding and Diagnosis | 3hrs |
| 3 | TB Treatment and Management | 7hrs |
| 4 | Program Management and Programmatic actions | 4hrs |
Chapter wise detailed instructions for Trainers
| Module 1: Basics of TB and NTEP | ||
| Chapter 1.1 | TB & TB Epidemiology | Mode: Self Learning |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Ask trainees: "Compare and discuss the prevalence of TB in your state and India" Refer to : National TB Prevalence survey 2019-2021 report, page 68 https://tbcindia.gov.in/WriteReadData/l892s/25032022161020NATBPSReport.pdf If there are other state specific estimates, discuss that. |
|
| Chapter 1.2 | NTEP | Mode: Self Learning |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
|
|
| Chapter 1.3 | Information Systems in NTEP | Mode: Self Learning |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Request all trainees to log into Ni-kshay using their institution's login credentials. Ask them to list various modules they are seeing on the page after logging in. | |
| Module 2: Case Finding and Diagnosis | ||
| Chapter 2.1 | General Concepts in TB Case Finding | Mode: Self Learning |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Ask a few trainees: 'If you refer 10 individuals with TB symptoms for testing from the OPD, what proportion will actually undergo testing?" Ask a follow up question: "How do you know that the number is correct?" Ask a follow up question: "What could be done to ensure that 100% of the clients referred are tested?" [ Getting information of all individuals with presumed TB either in Ni-kshay or other methods, specimen collection and transportation to prevent the leaks in cascade of care, monitoring the results against the line list of individuals with presumed TB] |
|
| Chapter 2.2 | Diagnostic Technologies and Lab Network | Mode: Self Learning |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Arrange a Visit to (a) Microscopy Centre and understand the External Quality Assurance activities (RBRC, OSE) happening (b) CB NAAT facility and observe the testing process (c) TrueNAT facility and observe the testing process | |
| Chapter 2.3 | Diagnostic Specimen | Mode: Self Learning |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: What is the Turn Around Time for various tests in your institution? How is that compared against the benchmark? How could we reduce it further? | |
| Chapter 2.4 | Active Case Finding Campaign | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
"A medical officer was reviewing the ACF data done in their field area. Total individuals mapped for ACF were 10,000; total individuals screened using TB symptoms were 8000. Out of them 400 were found to have TB symptoms. 200 underwent testing and 20 were diagnosed as TB, all were initiated on treatment" Provide them the scenario. Ask them to comment on the data. Discuss: Where is the biggest leaks in cascade? (significant leak in people with TB symptoms not underwent a test). What measures will you take as MO-PHI to minimize the gap? |
|
| Module 3: TB Treatment and Management | ||
| Chapter 3.1 | General Concepts in TB Treatment | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Physically check the Fixed Dose Combinations available in the program [4 FDC, 3 FDC, Pediatric drugs] Perform treatment initiation, and outcome declaration in demo version of Ni-kshay and restart a case to reinitiate the case on a new episode. |
|
| Chapter 3.2 | TB Treatment and Care | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
A 30-year-old female with 66 Kg, newly diagnosed to have drug sensitive pulmonary TB. 1. What pre-treatment evaluation will you advise before initiating the client on treatment? 2. Initiate and the treatment and prescribe the treatment on the demo version of Ni-kshay 3. Schedule clinical and laboratory follow-up for the client. What all will you will assess when she comes for the follow up? |
|
| Chapter 3.3 | Treatment Support | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
Discuss: How do you generally assign treatment supporter to your patient? Is that in consultation with the patient? Discuss: How many treatment supporters are in your area? What do you think about the quality of treatment support they provide? Share some experiences |
|
| Chapter 3.4 | Adherence Management | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity |
On the demo version of Ni-kshay, Mark adherence for a person on TB Treatment; 5 days as manually reported as taken and 5 days as manually reported as missed. Login to Ni-kshay using your institutional credentials. Comment on the treatment adherence pattern of the patients under anti-TB treatment in your area. |
|
| Chapter 3.5 | TB and comorbid conditions | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: How many people with diabetes are visiting your institution on a month? Are they all been screened for TB? Share your experiences related to screening for TB among the people with diabetes. How could we ensure that all people with diabetes reaching a health facility are screened for TB? | |
| Chapter 3.6 | Infection Prevention & Control | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: What are the various administrative measures for air borne infection control in your institutions? Is it adequate? Is there a scope for improvement? | |
| Chapter 3.7 | TB Preventive Therapy | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
TB Preventive Therapy is permitted only after ruling out TB TB preventive therapy is available for people at high risk of TB but is not currently diseased, such as contacts and PLHIV |
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: What proportion of eligible contacts in your area are initiated on TPT? Out of those whom you initiated, what proportion completes the TPT? What needs to be done to improve the situation | |
| Module 4: Program Management and Programmatic actions | ||
| Chapter 4.1 | Public Health Actions | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: What are the some of the communication practices towards a person affected with TB you wish to see changed from your colleagues/staff of your health facility? | |
| Chapter 4.2 | Patient Support | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: How should we support a person with TB with alcohol use disorder? Share your experiences related to your team's support in managing such clients. | |
| Chapter 4.3 | Social Inclusion and wellness activities | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: Do you think gender inequality in TB care exists in your area? As a MO-PHI, what can you do to address the same? | |
| Chapter 4.4 | Programme Monitoring | Mode: Self / virtual instructor led |
| Emphasis Points |
|
|
| Post Session Activity | Discuss: Is the Panchayat/Local Body where your health facility is located progressing towards ending TB? Discuss using data. | |
Competencies of MO-PHI
Competencies of MO-PHI| # | Competency | Description/ activities pertaining to the said competency | Assessment methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diagnose TB Correctly and completely based on NTEP guidelines/Standards of TB Care in India | - Identify individuals vulnerable to develop TB disease and TB Infection. - Screen for TB using 4 symptom complex and Chest X ray and identify presumptive TB - Prescribe appropriate diagnostic test to diagnose TB/ EP-TB, DR-TB, paediatric TB and TB Infection to the eligible based on NTEP guidelines/ Standards of TB Care in India - Enroll a person in Ni-kshay and request for Test through Ni-kshay based on NTEP Diagnostic algorithms and requirements for UDST - Enter the diagnosis details of clinically diagnosed TB in Ni-kshay - Implement Intensified Case Finding in the Facility |
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay to check whether correct tests are prescribed and the diagnosis is complete including testing for drug resistance 2. Interview with Medical Officer to understand his/her practice in relation to diagnosis of TB and adherence to diagnostic algorithm and request appropriate tests. 3. Assess OPD referral rates of presumptive TB Cases and random prescription audits for referral for TB Testing of presumptive TB Cases 4. Interviews with people affected with TB under care of the MO to check whether cases are diagnosed completely based on referral for testing and test results. 5. Review of Test Request (Referral for testing) Registers to check for appropriate referral of patients or their samples for higher diagnostic tests which are not available in the current health facility. |
Trainers Guides for Cadre wise Courses
Trainers Guides for Cadre wise Courses- Trainers' Guide for Health Volunteers Course
- Trainers' Guide for Pharmacists (SDS & DDS) Course
- Trainers' Guide for STS Course
- Trainers' Guide for STLS Course
- Trainers' Guide for LT (Microscopy & NAAT)
- Trainers Guide for CHO/MPW-PHI Course
- Trainers' Guide for Program Manager's course
- Trainers' Guide for MO-TC Course
Trainers' Guide for Course for MO-TC on NTEP
Trainers' Guide for Course for MO-TC on NTEPIntroduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the course coordinators and trainers for the ‘Course for Medical Officers- TB Control’ guidance for planning and executing the training. The targeted trainees for this course would be:
- Medical Officers- TB Control
This training may be provided by utilizing the blended approach where a mix of training methods and modes will be used to deliver content. This would include either in-person/ virtual training or facilitator led/ Self learning/ demonstration and role plays. Training sessions which require hands-on training will be conducted only in a physical setting. Keeping in mind the aforesaid best practices of the Modernized Training System, the training institute may decide to choose the approach which is most suitable for their trainees.
-
The training of MO-TC is to be conducted at STDCs. The batch size for Physical Session/Virtual Sessions should not be more than 25.
Virtual sessions: the trainees will be going through the online content, and attempt quizzes after each module. An instructor-led session will also be conducted for each module. This will help the trainees for better clarification of contents and to address the queries and doubts.
Physical/In-person Sessions: For the training areas which require hand-holding of trainees like demonstration of processes- like patient management in Ni-kshay, filling of various forms, Adherence Management tools, recording information on Public Health action, use of NI-kshay Aushadhi, etc in-person training sessions need to be conducted.
The training course content has 13 modules and 53 chapters. Based on different modalities used for the training, the training delivery should take at least 60 hours.
For the purpose of assessment of trainees, a pre-test before the beginning of training, interim quizzes at the end of each module and a post-test at the end of training has been configured in the course content.
Some exercises have also been formulated to assess and reinforce the learnings of the trainees based on their job requirements. These exercise will be communicated to the trainees either before the beginning of in-person sessions and the solutions of which will be discussed during the physical sessions.
The other exercises will be given to trainees during the conduct of the training and will be discussed simultaneously.The certificates are auto-generated for the trainees in their LMS account on successful completion of post-test and their performance in interim quizzes.
Training curriculum / Agenda
| Sr. | Module | Chapters | Training Modality |
Duration (Hrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basics of TB and NTEP |
|
Self-Reading/Virtual
|
6 |
|
2
|
TB Laboratories and Diagnostic technologies in NTEP |
|
Self-Reading/Virtual | 6 (including Lab/Field visit) |
| 3 | TB Diagnosis and Case finding |
|
Physical |
6
|
| 4 | TB Treatment |
|
Physical | 10(including field visit) |
| 5 | TB and comorbidity management |
|
Physical | 3 |
| 6 | Public Health Action |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 7 | TB Prevention |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 8 | Direct Benefit Transfer in NTEP |
|
Physical |
6
|
| 9 | Procurement, Supply Chain Management & Preventive Maintenance |
|
Physical | 6 |
| 10 | Partnerships, Corporate and Multisectoral engagement |
|
Physical | 4 |
|
11
|
ACSM and Community Engagement |
|
Physical | 4 |
|
12
|
Supervision, Monitoring and Evaluation |
|
Physical | 4 |
| 13 | Training and capacity development | Physical | 3 |
Trainers:
For this course, following personnel may be appointed as the trainers:
- MO - STDC
- MO - STC
- WHO-consultants
- DTO (select)
- SDS/DDS Pharmacists (Select)- for Supply chain and drug distribution module.
Trainer Eligibility
Trainers should have ability to conduct training in an interactive and interesting manner. The Trainers should have completed the ‘Course for MO-TC’ or Should have undergone training on 'Course for Program Managers in NTEP' and they must possess strong knowledge about the NTEP and the various processes related to patient workflow, Niskahy and Niskahy Aushadhi. The Trainers need to go through the Chapter- wise Training Guide for this Course, provided as an Annexure.
The Trainers should be well versed with the IT systems, for video conferencing (such as Zoom), Learning Management System (such as Swasth-eGurukul), Ni-kshay and Ni-kshay Aushadhi.
Chapter wise instructions for Trainers
The aim of providing chapter-wise detailed instructions provides the Trainers with the following:
- Module-wise and Chapter-wise, modality that may be adopted (Self-reading/virtual/ Physical/ In-person)
- The estimated time to complete the content.
- The key messages that a trainer should emphasize upon, while delivering the training
The activities which should be conducted at the end of each chapter / session to ensure learning effectiveness. This may include asking specific questions, demonstrating processes, discussing various forms and equipment. If any Module specific physical visits are required to be conducted, such details are also provided here.
Some exercises have also been provided with the relevant chapters that the trainees need to finish as the part of curriculum. The trainers should ensure that all the trainees finish these exercises individually and record it in appropriate response forms. All the exercise should be discussed by the trainers during the training.
This guiding document will also aid in bringing uniformity with respect to the content and quality of training conducted across the entire state and nation.
| Module 1: Basics of TB and NTEP | |
|---|---|
| Chapter 1.1 | TB & TB Epidemiology |
| Emphasis Points | 1. Difference between Incidence and notification 2. Difference between Exposure to TB, infection and TB disease. |
| Post Session Activity |
These exercises are to be given as assignments that trainees need to finish before start of 2nd module. Assignments:
|
| Chapter 1.2 | NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post Session Activity |
Discuss- ‘What India is committed to achieve in 2025 in relation to ending TB?’’ [Clarify that the country is only trying to achieve the SDG goals related to Ending TB] Discuss- ‘Can Medical College/ IRL be a PHI?’[Clarify that any patient service delivery point will be a PHI, but program management units like STC, DTC, TU etc are not PHIs] Assignments:
|
| Chapter 1.3 | Approaches to S&M in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the importance of S&M. Emphasize that S&M of the different activities under NTEP will be discussed alongside the activity while discussing the content in the modules. |
| Post-session activity |
Assignment: 1.3.1- Find the index score of your district using Nikshay for year 2022. |
| Chapter 1.4 | Integration of NTEP with Health System |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the need for integration of NTEP with the general health system & NHM and how that integration is envisioned. |
| Post-session activity |
Discuss - "What are the opportunities available to NTEP through Health & Wellness Centers? How could that be materialized? Assignments: 1.4.1-Write the organisation str of NTEP in your district. |
| Chapter 1.5 | Information Systems in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post-session Activity | 1.5.1- Enlist the different stakeholders that are working with Nikshay and their specific roles in NI-kshay. |
| Module 2 | TB Laboratories and Diagnostic technologies in NTEP |
| Chapter 2.1 | Diagnostic Technologies and Lab Network |
| Emphasis Points | Names of different tests, their uses, advantages and disadvantages |
| Post-session Activity |
Discuss: what are the advantages and disadvantages of FL- LPA over NAAT? Discuss “how many sputum collection and transportation facilities are there in their concerned district? Make one participant explain how it functions and what are the benefits out of it”? - Bring out the following benefits (1) prevents leaks in cascade of care (reduce loss from presumptive TB identification to TB Testing) (2) minimizes patient inconveniences (3) minimize patient Turnaround Time (4) reduce out of pocket expenditure (5) helps in infection control as people with symptoms need not travel Assignment: 3.1.1Learn about the processes being followed in your district for sample transport from patient to TDC. |
| Chapter 2.2 | TB detection Centres |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the consumables required for the Microscopy, CBNAAT and Truenat |
| Post-session Activity |
Assignments: A Lab-visit needs to be organised for participants to see the different processes involved for testing. |
| Chapter 2.3 | Specimen collection and transportation |
| Emphasis Points |
The need for SCT, importance of cool chain requirement. Discuss how the delays can be reduced to improve the TAT overall |
| Post Session Activity | May ask one of the participants to volunteer and demonstrate the different processes being followed in Nikshay for the same- i.e. adding test request, sample details and result updation in Ni-kshay. |
| Chapter 2.4 | Quality Assurance of TDC |
| Emphasis Points | Explain the process involved in EQA of microscopy. |
| Post-session Activity |
Lab Field visit: A field visit should be organized to a lab to understand and discuss the following:
3) Obtain the Lab register from Nikshay and calculate the patient TurnAroundTime (referral to test reporting) for the lab and compare it with the Lab TurnAroundTime (Sample Receipt to Reporting) |
| Module 3 |
TB Diagnosis and Case finding |
| Chapter 3.1 | General Concepts in TB Case Finding |
| Emphasis Points | Differentiate between screening and testing. |
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter 3.2 | Approaches to TB Case Finding |
| Emphasis Points | Clearly differentiate the difference between the three different approaches- Active, Passive and Intensified. |
| Post-session Activity |
(i) Screening for active TB in a Diabetic Clinic & testing those who screened positive (ii) Screening for active TB in an elderly home & testing those who screened positive (iii) Screening for active TB in cancer wards & testing those who screened positive |
| Chapter 3.3 | Diagnostic Algorithms in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss how the algorithms to be read |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to look at details of 5 TB patients from their TU and see whether complete diagnostic algo has been followed or not. |
| Chapter 3.4 | Active Case Finding Campaign |
| Emphasis Points | Step by step process in planning and execution of an ACF campaign with special emphasis on identification of target population, need for micro planning and need to prevent the leaks in the cascade of care. |
| Post-session Activity | Discuss how ACF campaign is carried in participants geography and how the activity can be carried out more effectively. |
| Chapter 3.5 | S&M for Case finding activities in NTEP. |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the TB index dashboard. Discuss the TB Notification dashboard. |
| Post-session Activity | The participants may be asked to access the TB index dashboard and TB notification dashboard from their logins and share their learnings with other audience. |
| Module 4 | TB Treatment |
| Chapter 4.1 | General Concepts in TB Treatment |
| Emphasis Points |
It's an overview chapter explaining the concepts- Fixed Dose Combination, Intensive & Continuation Phase.
|
| Post-session Activity | Request two participants to demonstrate in Demo Ni-kshay the ‘Transfer’ of patients using (i) Push and (ii) Pull methods. |
| Chapter 4.2 | ADRs to ATT |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss about the aDSM available in Ni-kshay , the importance and how it is carried out. |
| Post-session Activity | Ask one of the participants to demonstrate the adverse event module in Ni-kshay from reporting, management and outcome. |
| Chapter 4.3 | DS-TB Treatment and Care |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 4.4 | Overview of DR-TB |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain:
|
| Post-session Activity | Ask participants for doubts and help them clear those doubts. |
| Chapter 4.5 | Isoniazid [H] Mono/Poly DR-TB Regimen |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the regimen composition and duration, inclusion-exclusion criterion, replacement sequence and the follow-up examination. |
| Post-session Activity | May ask the participant to look at 2 TB patients (outcome declared) on H Mono/poly DR-TB regimen whether the follow-up sputum examination was done timely or not. |
| Chapter | Shorter Oral Bedaquiline-containing MDR/RR-TB Regimen |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the regimen composition and duration, inclusion-exclusion criterion, replacement sequence and the follow-up examination. |
| Post-session activity | May ask participants to look at 2 TB patients (outcome declared) on shorter oral Bdq containing MDR/RR regimen whether all the relevant investigations for PTE and follow-up sputum examination were carried out timely. |
| Chapter | Longer Oral M/XDR-TB Regimen |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the regimen composition and duration, inclusion-exclusion criterion, replacement sequence and the follow-up examination. |
| Post-session activity | May ask participants to look at 1 TB patient (outcome declared) on longer oral M/XDR regimen whether all the relevant investigations for PTE and follow-up sputum examination were carried out timely. |
| Chapter 4.6 | Treatment Support |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the role of treatment supporter and how they can be registered in Nikshay, patient mapped. |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to practice the registration of treatment supporter and subsequent mapping of patients to the treatment supporters in demo-version in Ni-kshay. |
| Chapter 4.7 | Adherence Management |
| Emphasis Points |
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter | Monitoring of Treatment |
| Emphasis Points | Discuss the indicators used in monitoring the treatment- treatment initiation, outcome declaration. |
| Post-session activity |
Exercise: Ask the participants to download the notification register for Q1-2023 and ask them to calculate the average delay in treatment initiation from date of diagnosis. Discuss how this delay can be minimised. |
| Field Activity |
A 2nd field visit(Batch size- 5-7 participants) should be organised to the following
|
| Module 5 |
TB and comorbidity management |
| Chapter 5.1 | TB and HIV |
| Emphasis Points | Bidirectional screening for TB-HIV |
| Post-session activity | Ask the participants to describe the existing mechanism at their district to screen TB among the people visiting ICTC centres- how is the screening being done? How is it ensured that all those referred for testing have undergone testing? Discuss if there is any scope for improvement. |
| Chapter 5.2 | TB and Diabetes |
| Emphasis Points | Bidirectional screening for TB-Diabetes |
| Post-session activity | Ask the participant to describe how diabetes testing is done among people with TB in their district? What are the steps if a person with TB is found to have diabetes? Who and how is diabetic control ensured for that person? Discuss if there are any ways to improve. |
| Chapter | TB and malnourishment |
| Emphasis Point: | Discuss how malnourishment affects TB patient and role of Nutritional support in successful completion of treatment. |
| Chapter | TB and Substance Abuse |
| Emphasis Point: | Discuss how Alcohol and Tobacco Abuse affects TB and importance of linkage with the deaddiction centre. |
| Post Session Activity | The participants may be asked to list the de-addiction centres and tobacco-caseation centres. |
| Chapter | TB and other comorbid conditions |
| Module 6 | Public Health Action |
| Chapter 6.1 | Patient Support |
| Emphasis Points | Various kinds of support the TB patient needs (nutritional support, psychosocial support, support for deaddiction, travel support) and how STS could help in offering the same |
| Post-session activity | Give a scenario: A 62-year-old woman from a Tribal community affected with TB. Ask all participants to list out all the Government schemes/initiatives which can support her during the treatment period? Write down all schemes in a flip chart/Chatbox/Virtual board |
| Chapter 6.2 | Contact tracing and investigation. |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 6.3 | Counselling |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 6.4 | TB Arogya Sathi App |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the various information available in TB Arogya Sathi Application-
|
| Post-session Activity | The participants may be requested to do a screening test on themselves and check the working of the application. |
| Module 7 | TB Prevention |
| Chapter 7.1 | Infection Prevention and Control |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Chapter 7.2 | TB Preventive Treatment |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to download the Contact tracing register (for Q3-2022) and comment on the leakages in the cascade of care for TPT for your geography. |
| Chapter 8.1 | General Concepts in DBT |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter 8.2 | Processes in DBT |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter 8.3 | Monitoring of DBT |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity |
|
| Module | Financial management and Planning |
| Chapter 9.1 | Overview of PIP |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | May ask the participants for any doubts/queries. |
| Chapter 9.2 | Needs assessment for Planning |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points:
|
| Post-session Activity | May ask the participants to clear their doubts |
| Chapter 9.4 | Financial expenditure and accounting |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain the following.
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Module | Procurement, Supply Chain Management & Preventive Maintenance |
| Chapter | General Concepts in SCM |
| Emphasis Points |
Explain the following concepts:
|
| Post-session Activity | |
| Chapter | Information system for SCM in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following: Ni-kshay Aushadhi Different dashboards- State/district/Alert/Reports and features available at different levels. |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participants to open their TU dashboard and look at the alert dashboard and share the finding with other participants. |
| Chapter | Processes in NTEP |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss and demonstrate the participants the following processes:
|
| Post-session Activity |
Ask the participant to demonstrate the following in demo version of Ni-kshay AUshadhi:
Ask the participants to demonstrate the following in demo version of Nikshay
Ask the participants to forecast the supplies (for DS-TB drugs) for next quarter on the basis of consumptions based in previous quarter in their TU. |
| Chapter | Quality Assurance in Supply Chain Management |
| Emphasis Points |
Discuss the following points: Meaning and Processes involved in QA of drugs in NTEP Recording of QA of drugs in Ni-kshay AUshadhi Monitoring of drug stores Store visits in NTEP- checklist for store visits Physical verification of supplies and recording in Ni-kshay Aushadhi |
| Post-session Activity | Ask the participant to open demo Ni-kshay aushadhi and demonstrate the recording of Physical Stock verification, and QA of drugs |
Competencies of the Medical Officers TB Centre- [MO-TC]
Competencies of the Medical Officers TB Centre- [MO-TC]Following are the competencies required for a Medical Officer TC
| # | Competency | Description | Competency Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diagnose TB Correctly and completely based on NTEP guidelines |
|
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay to check whether correct tests are prescribed and the diagnosis is complete including testing for drug resistance 2. Interview with Medical Officer to understand his/her practice in relation to diagnosis of TB and adherence to diagnostic algorithm and request appropriate tests. 3. Assess OPD referral rates of presumptive TB Cases and random prescription audits for referral for TB Testing of presumptive TB Cases 4. Interviews with people affected with TB under care of the MO to check whether cases are diagnosed completely based on referral for testing and test results. 5. Review of Test Request (Referral for testing) Registers to check for appropriate referral of patients or their samples for higher diagnostic tests which are not available in the current health facility. |
| 2 | Prescribe and initiate correct TB treatment to a person diagnosed as TB/ TBI |
|
1. Verification of case records and treatment card in Ni-kshay to check whether correct regimens are prescribed 2. Interview with Medical Officer to understand current prescription practices 3. Interview with patients under care of MO and assess whether right regimen are prescribed 4. Review of Ni-kshay module for differentiated TB care which is updated for all the patients for the TB unit |
| 3 | Perform pre-during and post-treatment evaluation of people affected with TB/DR-TB/TB Infection, as per NTEP guidelines |
|
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay/ Treatment cards or prescriptions to check whether all evaluations are done correctly 2. Interview with the Medical Officer to understand the current practice of pre-during-post evaluations 3. Interview with patients/beneficiaries under the MO's care to check whether all evaluations are done correctly 4. Review Status of post Treatment follow-up in cases notified in Ni-kshay for the past year |
| 4 | Identify and manage Adverse Drug Reactions due to anti-TB drugs |
|
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay and treatment records to see ADR's were identified and managed 2. Interview with Medical Officer to understand the practices related to ADR identification and management, including referral to higher centers 3. Interview with patients/beneficiaries under MO's care to understand whether ADRs are identified and managed properly |
| 5 | Refer correctly and timely, a person affected with TB/DR-TB, to higher center/ nearest health facility for appropriate management |
|
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay and treatment records to check whether referral is correct and timely 2. Interview with MO to understand the current practice related to referral 3. Interview patients/beneficiaries under MO's care to check whether referral is prompt |
| 6 | Evaluate and mange person affected with TB for medical co-morbidities and conditions |
|
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay to check whether screening and management of co-morbidity are done as per guidelines 2. Interview MO to understand current practices regarding co-morbidity management 3. Interview beneficiaries/ patients under MO's care to check whether co-morbidities are screened and managed properly |
| 7 | Counsel the people with presumptive TB or people affected with DS-TB/DR-TB/ TBI and their family |
|
1. Interview with Medical Officer to understand current practices regarding counselling 2. Interview with patients/ beneficiaries to understand the quality of counselling received from MO |
| 8 | Ascertain treatment outcomes as per NTEP guidelines |
|
1. Verification of records in Ni-kshay to check whether outcome assigned are correct 2. Interview with people who had their outcome assigned to check whether the outcome assigned were correct |
| 9 | Monitor NTEP and perform supportive supervision in the health facility and in the population served by the health facility |
|
1. Verification of review meeting minutes, documentation of feedbacks provided and supervisory registers to check quality of monitoring, review and supervision activities 2. Interview with MO to understand the current practices regard to Monitoring, Review and Supportive supervision 3. Interview with staff (ANM, ASHA, TB HV, STS, MPHW, CHO, Nurse, Pharmacist etc.) supervised by MO to get an understanding about the quality of supportive supervision and review |
| 10 | Advocate with Local Government, Private providers and community for engaging them for TB Elimination activities in the field area of health facility |
|
1. Check for any results of advocacy in terms of commitment from Local Government, engagement of private providers, engagement of community 2. Interview with private practitioners and Local Government leaders to get an understanding about the MO's competency |
[Draft] Trainers Guide for Course for Senior DR-TB/TB-HIV Supervisor on NTEP
[Draft] Trainers Guide for Course for Senior DR-TB/TB-HIV Supervisor on NTEPIn Development
Competencies of Sr DR-TB/TB-HIV Supervisor
Competencies of Sr DR-TB/TB-HIV SupervisorThe following competencies are essential to a Sr DR-TB/TB-HIV Supervisor.
| # | Competency | Description | Assessment Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Monitor and coordinate for DST/DRT Testing for all Notified TB Cases | - Identify individuals pending various DST/ DRT tests from Notification Register/ Patient wise Lab register based on NTEP guidelines - Coordinate with various field staff to obtain samples and transport them to linked Laboratory and to obtain valid results, and ensure Patient TATs are within norms - Reinitiate new epsiodes and initiate request for Test through Ni-kshay |
Evaluate knowledge, attitude, and practices based on a review of the status of DST/DRT Testing performance in the district. |
| 2 | Coordinate to initiate appropriate DRTB treatment by referral to relevant PHI and coordinate with field staff for patient support | - Check the reports of various laboratory investigations and coordinate to establish the diagnosis of DRTB - Refer a person with TB to the appropriate DRTB Centre/ ART Centre/ health facility for Clinical followup/ Treatment initiation and ensure appropriate HF Linkage in Ni-Akshay -Co-ordinate to identify an appropriate treatment supporter and health facility in consultation with the medical officer, field staff and beneficiary -Document the treatment initiation and details of prescription in Ni-kshay |
1. Verification of case records in Ni-kshay to check whether correct regimens are prescribed when new diagnostic information is available 2. Interview with patients under care of the individual to check whether treatment initiation is as per NTEP guidelines |
| 3 | Counsel the people who are presumptive DRTB/ diagnosed with/ on treatment for, DR-TB and their family | Through home visits Counsel the people with presumptive DR-TB/ people diagnosed with or on treatment of DR-TB and TB-HIV on: -Early and complete Diagnosis of DRTB, correct and complete Treatment of DRTB, -Treatment Adherence, -Co-morbidity management including regular Treatment and follow-up with ART for PLHIV -Airborne Infection Control, -Contact Investigation, -TB Preventive Therapy for contacts, -Adverse Drug Reaction monitoring and management -Social welfare measures |
1. Interview with people affected with TB/TBI to check STS's ability to counsel |
| 4 | Monitor the treatment adherence of people on DR-TB treatment and initiate timely retrieval actions |
-Monitor treatment adherence records on Niksay on a day to day basis -Identify people who have missed doses -Investigate reasons for missed doses and trouble shoot -Initiate timely retrieval actions wherever required |
1. Review Ni-kshay adherence calenders 2. Interview with treatment supporters and patients who missed doses |
| 5 | Coordinate timely Clinical and Laboratory follow-up of DR-TB patients according to NTEP Guidelines | Clinical Followup Laboratory Followup Treatment outcomes Long Term Post Treatment Outcomes |
|
| 6 | Monitor Status of completion of comorbidity Testing for All notified TB patients | Coordinate with NTEP staff for timely completion of comorbidity testing | . Review in Ni-kshay reports and register |
| 7 | Monitor and Raise a request for drug stock and consumables replenishment at particular health facility | - To monitor adherence to stocking norms and identify health facility for impending stockouts or with drug stock nearing expiry and assist respective PHI drug store to raise refill request. - Coordinate with DTC/ State drug store pharmacist for issuance of relevant drug stock as per request |
1. Review indent and issue register of Ni-Kshay Aushadhi |
| 8 | Support the DTO in organizing the District level Comorbidity Committees and ensure optimal performance of TB Comorbidity activities |
-Prepare and maintain a directory of ICTCs, ART Centres, Community Care Centres, NCD clinics, private health facilities and NGOs working for HIV , in the district and collaborating NTEP Centres -Coordinating the meeting with relevant stakeholders and preparing action points -To oversee that action points are implemented
|
|
| 9 | Build capacity of District staff (STS/ TBHV, MPHW, TS/HV, CHO) on DR-TB Services | - Support in the training of Peripheral staff |
1.Competency Assessment |
| 10 | Assist DTO to monitor the NTEP in the district | - Use Ni-kshay dashboards and other program reccords, and interpret key performance indicators of NTEP in the faility/geography -Perform time, place, person analysis and identify areas for improvement ` -Assist MO in Monitoring the input and process indicators related to the output/outcome indicator and suggest corrective actions - Conduct supportive supervision and help in building the capacity of treatemnet supporters with an intention to improve quality of services. - Assist Medical Officer in providing timely and actionable feedback to health sub-centers and reporting field staff (ANM, ASHA, TB-HV, STS, STLS, MPW, HA, etc.) - Support the staff in taking the corrective actions leading to an improvement in quality of services" |
1. Interview with DTO/ MO-DTC to check ability in supporting monitoring 2. Verification of review meeting minutes & documentation of feedback provided |