Content Status
Type
Linked Node
Supervision by STS
Learning ObjectivesWho all to supervise, what to supervise, how to supervise
The Senior Treatment Supervisor (STS) is a part of the Tuberculosis Unit (TU) team at the sub-district level in the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
The STS is responsible for supervising the treatment of the patients and works closely with treatment supporters and Primary Health Care system.
The objective of these supervisory visits is to supervise patients' treatment and to monitor the programme at the TU level. They also support the treatment supporters to carry out their role efficiently and troubleshoot the issue that they might face.
The visits by STS are conducted on a systematic basis and the protocol to be followed during these visits is shown in the figure below.
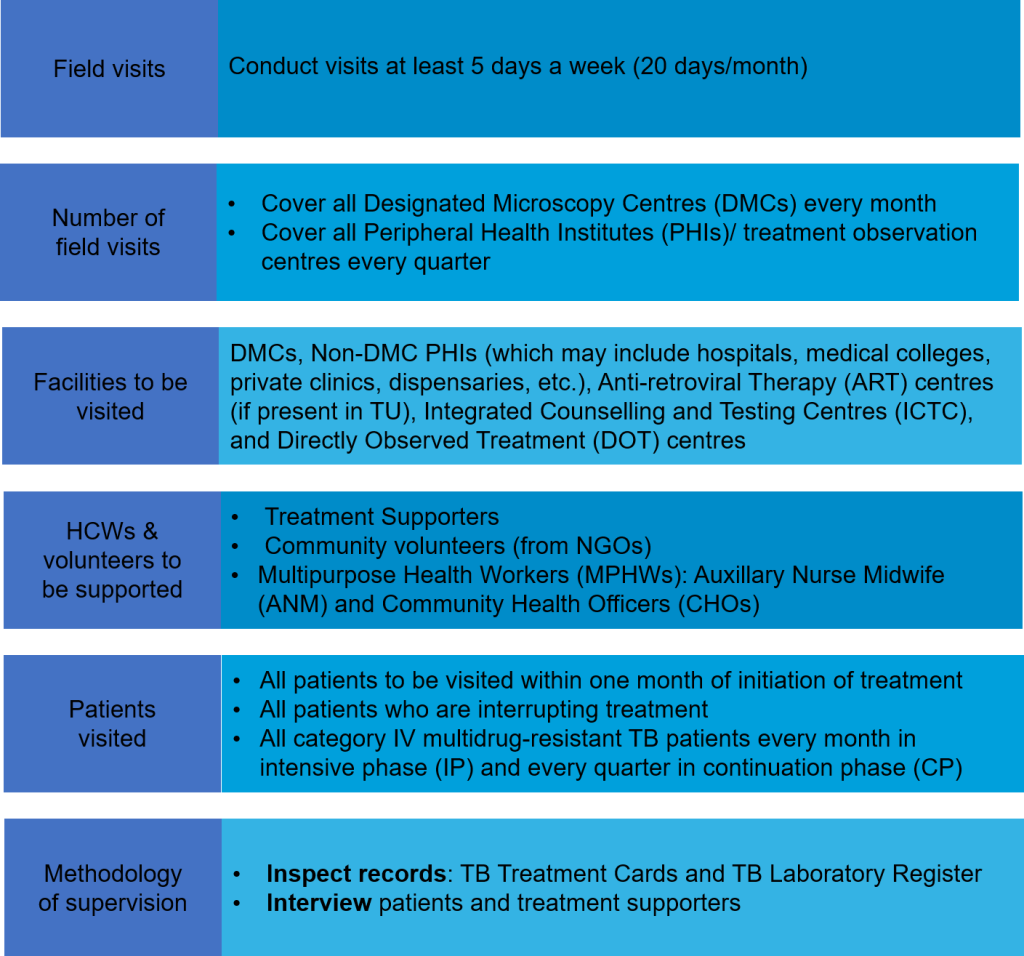
Figure: Supervisory Protocols for the STS
Supervisory Checklist for the STS
A supervisory checklists can be used by the STS to make sure that s/he does not miss any aspect during the visit. In summary, the STS must supervise the following:
- Facility assessment:
- Anti-TB drugs: Assess for storage conditions (including if First-Expired, First-Out (FEFO) is followed), stock availability and stock-outs.
- Infrastructure: Presence and condition of physical spaces (including cleanliness) for patient consultation and waiting areas, availability of functional X-ray units (in case of X-ray centres) and weighing scales.
- Supplies: Assess the quantity of supplies such as sputum containers, forms, and treatment cards.
- Case detection and diagnosis: Check if all persons with presumed TB identified were referred for diagnosis, check referral in Nikshay and specimen processed, check for any losses, check if all specimen collected reached laboratory and examined. Check if all diagnosed are tacked correctly.
- Treatment: This includes monitoring for:
- Early treatment initiation, entry in Nikshay (Notification), and allocation of treatment supporter.
- Appropriate medicine dosage by weight and type.
- Alternative resources mobilised for treatment observation.
- DOT for every dose in the Intensive Phase (IP) of treatment.
- Universal Drug Susceptibility Testing
- Prompt follow up sputum examinations
- Acceptability of the treatment supporter to the patient
- Prompt treatment tectorial efforts for interrupting patients
- Recording and Reporting: This includes:
- Ensuring all patients are correctly registered in Nikshay
- Proper updation of treatment schedules and doses, including retrival actions in Nikshay by the treatment supporter
- All treatment supporters are given Nikshay credentials, their Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) entered in the Nikshay properly
- DBT of the patients correctly recorded in the nikshay portal
- DBT of the private providers are recorded correctly in the Nikshay portal
5. Patient interviews: The STS should check the following:
- TB knowledge: If the patient knows about TB, its symptoms, drugs prescribed, duration of treatment, consequences of irregular/ incomplete treatment, frequency and importance of follow up tests, and importance of examining symptomatic close contact persons.
- Monitoring: If they are receiving DOTS as prescribed, if the Peripheral Health Worker (PHW) knows their home, frequency of home visits during IP/ Continuation Phase (CP)/ missed doses, and if help from family members/ others was ever enlisted.
6. Supportive supervision with on job capacity building:
- The STS is expected to build the capacity of treatment supporter during the field visit. Build their capacity by
- Demonstrating Nikshay portal entry
- Imparting skills on the patient support system (guiding, counselling, contact tracing, treatment retrieval, Adverse Drug Reaction management, DBT and other social schemes etc)
Resources
- Module for Senior Treatment Supervisors, RNTCP, 2005.
- Training Modules (1-4) for Programme Managers and Medical Officers, 2020.
Assessment
| Question | Answer 1 | Answer 2 | Answer 3 | Answer 4 | Correct answer | Correct explanation | Page id | Part of Pre-test | Part of Post-test |
| How often should an STS visit a PHI in their area? | Once a month | Twice a month | Every quarter | Every day | 3 | Senior Treatment Supervisors (STS) should cover all PHIs/ treatment observation centres every quarter. | Yes | Yes | |
| The STS can involve themselves in role plays to communicate key health messages. | TRUE | FALSE | 1 | Senior treatment supervisors can involve themselves in role plays with MPWs/ DOTS providers to communicate key health messages. | Yes | Yes |
Content Creator
Reviewer
Target Audience
- Log in to post comments